Page 76 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 76
Plate 3-11 Integumentary System
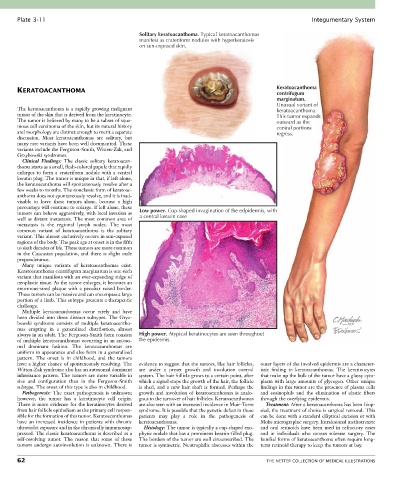
Solitary keratoacanthoma. Typical keratoacanthomas
manifest as crateriform nodules with hyperkeratosis
on sun-exposed skin.
Keratoacanthoma
KERATOACANTHOMA centrifugum
marginatum.
Unusual variant of
The keratoacanthoma is a rapidly growing malignant keratoacanthoma.
tumor of the skin that is derived from the keratinocyte. This tumor expands
The tumor is believed by many to be a subset of squa- outward as the
mous cell carcinoma of the skin, but its natural history central portions
and morphology are distinct enough to merit a separate regress.
discussion. Most keratoacanthomas are solitary, but
many rare variants have been well documented. These
variants include the Ferguson-Smith, Witten-Zak, and
Grzybowski syndromes.
Clinical Findings: The classic solitary keratoacan-
thoma starts as a small, flesh-colored papule that rapidly
enlarges to form a crateriform nodule with a central
keratin plug. The tumor is unique in that, if left alone,
the keratoacanthoma will spontaneously resolve after a
few weeks to months. The nonclassic form of keratoac-
anthoma does not spontaneously resolve, and it is inad-
visable to leave these tumors alone, because a high
percentage will continue to enlarge. If left alone, these
tumors can behave aggressively, with local invasion as Low power. Cup-shaped invagination of the edpidermis, with
well as distant metastasis. The most common area of a central keratin core
metastasis is the regional lymph nodes. The most
common variant of keratoacanthoma is the solitary
variant. This almost exclusively occurs in sun-exposed
regions of the body. The peak age at onset is in the fifth
to sixth decades of life. These tumors are more common
in the Caucasian population, and there is slight male
preponderance.
Many unique variants of keratoacanthomas exist.
Keratoacanthoma centrifugum marginatum is one such
variant that manifests with an ever-expanding ridge of
neoplastic tissue. As the tumor enlarges, it becomes an
enormous-sized plaque with a peculiar raised border.
These tumors can be massive and can encompass a large
portion of a limb. This subtype presents a therapeutic
challenge.
Multiple keratoacanthomas occur rarely and have
been divided into three distinct subtypes. The Gryz-
bowski syndrome consists of multiple keratoacantho-
mas erupting in a generalized distribution, almost
always in an adult. The Ferguson-Smith form consists High power. Atypical keratinocytes are seen throughout
of multiple keratoacanthomas occurring in an autoso- the epidermis.
mal dominant fashion. The keratoacanthomas are
uniform in appearance and also form in a generalized
pattern. The onset is in childhood, and the tumors
have a higher chance of spontaneously resolving. The evidence to suggest that the tumors, like hair follicles, outer layers of the involved epidermis are a character-
Witten-Zak syndrome also has an autosomal dominant are under a preset growth and involution control istic finding in keratoacanthomas. The keratinocytes
inheritance pattern. The tumors are more variable in system. The hair follicle grows to a certain point, after that make up the bulk of the tumor have a glassy cyto-
size and configuration than in the Ferguson-Smith which a signal stops the growth of the hair, the follicle plasm with large amounts of glycogen. Other unique
subtype. The onset of this type is also in childhood. is shed, and a new hair shaft is formed. Perhaps the findings in this tumor are the presence of plasma cells
Pathogenesis: The exact pathogenesis is unknown; growth and involution of keratoacanthomas is analo- and eosinophils and the elimination of elastic fibers
however, the tumor has a keratinocyte cell origin. gous to the turnover of hair follicles. Keratoacanthomas through the overlying epidermis.
There is more evidence for the keratinocytes derived are also seen with an increased incidence in Muir-Torre Treatment: After a keratoacanthoma has been biop-
from hair follicle epithelium as the primary cell respon- syndrome. It is possible that the genetic defect in these sied, the treatment of choice is surgical removal. This
sible for the formation of this tumor. Keratoacanthomas patients may play a role in the pathogenesis of can be done with a standard elliptical excision or with
have an increased incidence in patients with chronic keratoacanthomas. Mohs micrographic surgery. Intralesional methotrexate
ultraviolet exposure and in the chronically immunosup- Histology: The tumor is typically a cup-shaped exo- and oral retinoids have been used in refractory cases
pressed. The classic keratoacanthoma is described as a phytic nodule that has a prominent keratin-filled plug. and in individuals who cannot tolerate surgery. The
self-resolving tumor. The reason that some of these The borders of the tumor are well circumscribed. The familial forms of keratoacanthoma often require long-
tumors undergo autoinvolution is unknown. There is tumor is symmetric. Neutrophilic abscesses within the term retinoid therapy to keep the tumors at bay.
62 THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS