Page 87 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 87
Plate 4-2 Rashes
ACNE VULGARIS
ACNE
Acne is an almost universal finding in teenagers across
the globe. Acne vulgaris is the most common form of
acne; it affects almost every human at some point in
their lifetime. Most cases are mild and do not cause any
significant disease. Most acne vulgaris is seen in the
postpubertal years. Many clinical variants exist, and
excellent therapeutic modalities are available to treat
this skin disease.
Clinical Findings: Acne vulgaris typically begins
soon after puberty. It has no racial or gender prefer-
ence, although males may develop more severe cases of
the disease. The first signs of acne development are the
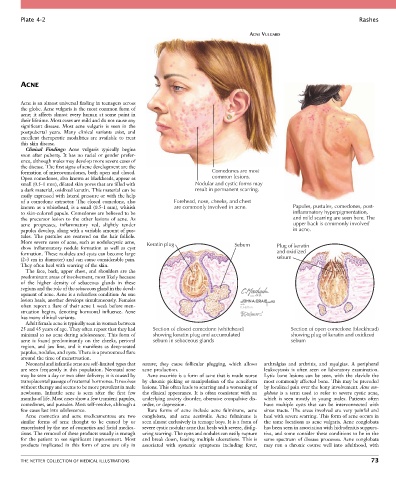
formation of microcomedones, both open and closed. Comedones are most
Open comedones, also known as blackheads, appear as common lesions.
small (0.5-1 mm), dilated skin pores that are filled with Nodular and cystic forms may
a dark material, oxidized keratin. This material can be result in permanent scarring.
easily expressed with lateral pressure or with the help
of a comedone extractor. The closed comedone, also Forehead, nose, cheeks, and chest
known as a whitehead, is a small (0.5-1 mm), whitish are commonly involved in acne. Papules, pustules, comedones, post-
to skin-colored papule. Comedones are believed to be inflammatory hyperpigmentation,
the precursor lesion to the other lesions of acne. As and mild scarring are seen here. The
acne progresses, inflammatory red, slightly tender upper back is commonly involved
papules develop, along with a variable amount of pus- in acne.
tules. The pustules are centered on the hair follicle.
More severe cases of acne, such as nodulocystic acne, Keratin plug Sebum
show inflammatory nodule formation as well as cyst Plug of keratin
formation. These nodules and cysts can become large and oxidized
(2-3 cm in diameter) and can cause considerable pain. sebum
They often heal with scarring of the skin.
The face, back, upper chest, and shoulders are the
predominant areas of involvement, most likely because
of the higher density of sebaceous glands in these
regions and the role of the sebaceous gland in the devel-
opment of acne. Acne is a relentless condition: As one
lesion heals, another develops simultaneously. Females
often report a flare of their acne 1 week before men- with
E. Hatton
struation begins, denoting hormonal influence. Acne
has many clinical variants.
Adult female acne is typically seen in women between
25 and 45 years of age. They often report that they had Section of closed comedone (whitehead) Section of open comedone (blackhead)
minimal to no acne during adolescence. This form of showing keratin plug and accumulated showing plug of keratin and oxidized
acne is found predominantly on the cheeks, perioral sebum in sebaceous glands sebum
region, and jaw line, and it manifests as deep-seated
papules, nodules, and cysts. There is a pronounced flare
around the time of menstruation.
Neonatal and infantile acne are self-limited types that nature; they cause follicular plugging, which allows arthralgias and arthritis, and myalgias. A peripheral
are seen frequently in this population. Neonatal acne acne production. leukocytosis is often seen on laboratory examination.
may be seen a day or two after delivery; it is caused by Acne excoriée is a form of acne that is made worse Lytic bone lesions can be seen, with the clavicle the
transplacental passage of maternal hormones. It resolves by chronic picking or manipulation of the acneiform most commonly affected bone. This may be preceded
without therapy and seems to be more prevalent in male lesions. This often leads to scarring and a worsening of by localized pain over the bony involvement. Acne con-
newborns. Infantile acne is seen after the first few the clinical appearance. It is often coexistent with an globata is a term used to refer to severe cystic acne,
months of life. Most cases show a few transient papules, underlying anxiety disorder, obsessive compulsive dis- which is seen mostly in young males. Patients often
comedones, and pustules. Most self-resolve, although a order, or depression. have multiple cysts that can be interconnected with
few cases last into adolescence. Rare forms of acne include acne fulminans, acne sinus tracts. The areas involved are very painful and
Acne cosmetica and acne medicamentosa are two conglobata, and acne aestivalis. Acne fulminans is heal with severe scarring. This form of acne occurs in
similar forms of acne thought to be caused by or seen almost exclusively in teenage boys. It is a form of the same locations as acne vulgaris. Acne conglobata
exacerbated by the use of cosmetics and facial medica- severe cystic nodular acne that heals with severe, disfig- has been seen in association with hidradenitis suppura-
tions. The removal of these products usually is enough uring scarring. The cysts and nodules can easily rupture tiva, and some consider these conditions to be in the
for the patient to see significant improvement. Most and break down, leaving multiple ulcerations. This is same spectrum of disease processes. Acne conglobata
products implicated in this form of acne are oily in associated with systemic symptoms including fever, may run a chronic course well into adulthood, with
THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS 73