Page 92 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 92
Plate 4-7 Integumentary System
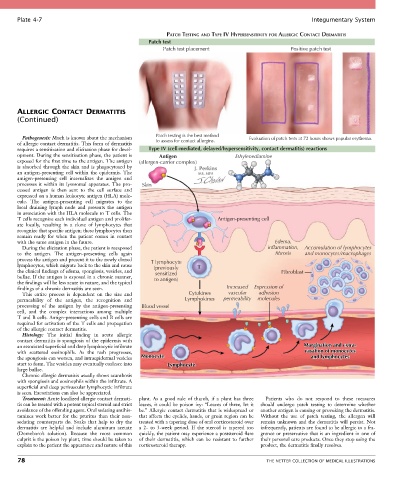
PATCH TESTING AND TYPE IV HYPERSENSITIVITY FOR ALLERGIC CONTACT DERMATITIS
Patch test
Patch test placement Positive patch test
ALLERGIC CONTACT DERMATITIS
(Continued)
Pathogenesis: Much is known about the mechanism Patch testing is the best method Evaluation of patch tests at 72 hours shows papular erythema.
of allergic contact dermatitis. This form of dermatitis to assess for contact allergins.
requires a sensitization and elicitation phase for devel- Type IV (cell-mediated, delayed/hypersensitivity, contact dermatitis) reactions
opment. During the sensitization phase, the patient is Antigen Ethylenediamine
exposed for the first time to the antigen. The antigen (allergen-carrier complex)
is absorbed through the skin and is phagocytosed by
an antigen-presenting cell within the epidermis. The
antigen-presenting cell internalizes the antigen and
processes it within its lysosomal apparatus. The pro- Skin
cessed antigen is then sent to the cell surface and
expressed on a human leukocyte antigen (HLA) mole-
cule. The antigen-presenting cell migrates to the
local draining lymph node and presents the antigen
in association with the HLA molecule to T cells. The
T cells recognize each individual antigen and prolifer- Antigen-presenting cell
ate locally, resulting in a clone of lymphocytes that
recognize that specific antigen; these lymphocytes then
remain ready for when the patient comes in contact
with the same antigen in the future. Edema,
During the elicitation phase, the patient is reexposed inflammation, Accumulation of lymphocytes
to the antigen. The antigen-presenting cells again fibrosis and monocytes/macrophages
process the antigen and present it to the newly cloned T lymphocyte
lymphocytes, which migrate back to the skin and cause (previously T
the clinical findings of edema, spongiosis, vesicles, and sensitized Fibroblast
bullae. If the antigen is exposed in a chronic manner, to antigen)
the findings will be less acute in nature, and the typical
findings of a chronic dermatitis are seen. Increased Expression of
This entire process is dependent on the size and Cytokines vascular adhesion
permeability of the antigen, the recognition and Lymphokines permeability molecules
processing of the antigen by the antigen-presenting Blood vessel
cell, and the complex interactions among multiple
T and B cells. Antign-presenting cells and B cells are
required for activation of the T cells and propagation
of the allergic contact dermatitis.
Histology: The initial finding in acute allergic
contact dermatitis is spongiosis of the epidermis with
an associated superficial and deep lymphocytic infiltrate Margination and extra-
with scattered eosinophils. As the rash progresses, vasation of monocytes
the spongiosis can worsen, and intraepidermal vesicles Monocyte and lymphocytes
start to form. The vesicles may eventually coalesce into Lymphocyte
large bullae.
Chronic allergic dermatitis usually shows acanthosis
with spongiosis and eosinophils within the infiltrate. A
superficial and deep perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate
is seen. Excoriations can also be appreciated.
Treatment: Acute localized allergic contact dermati- plant. As a good rule of thumb, if a plant has three Patients who do not respond to these measures
tis can be treated with a potent topical steroid and strict leaves, it could be poison ivy: “Leaves of three, let it should undergo patch testing to determine whether
avoidance of the offending agent. Oral sedating antihis- be.” Allergic contact dermatitis that is widespread or another antigen is causing or provoking the dermatitis.
tamines work better for the pruritus than their non- that affects the eyelids, hands, or groin region can be Without the use of patch testing, the allergen will
sedating counterparts do. Soaks that help to dry the treated with a tapering dose of oral corticosteroid over remain unknown and the dermatitis will persist. Not
dermatitis are helpful and include aluminum acetate a 2- to 3-week period. If the steroid is tapered too infrequently, patients are found to be allergic to a fra-
(Domeboro’s solution). Because the most common quickly, the patient may experience a poststeroid flare grance or preservative that is an ingredient in one of
culprit is the poison ivy plant, time should be taken to of their dermatitis, which can be resistant to further their personal care products. Once they stop using the
explain to the patient the appearance and nature of this corticosteroid therapy. product, the dermatitis finally resolves.
78 THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS