Page 354 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 354
320 Chapter 11
1 sec <3 sec 1 sec 3 sec 1 sec 3 sec 1 sec
I E I E I E I
V (Liter) 0.8
V (L/min) 50 2 4 6 8 10 12
2 4 6 8 10 12
260
P (cm H 2 O) 40
© Cengage Learning 2014
2 4 6 8 10 12
Time (sec)
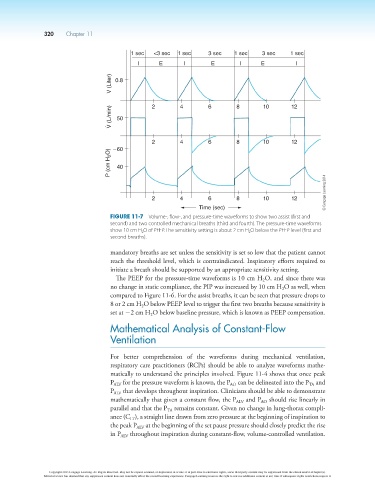
Figure 11-7 Volume-, flow-, and pressure-time waveforms to show two assist (first and
second) and two controlled mechanical breaths (third and fourth). The pressure-time waveforms
show 10 cm H 2 O of PEEP. The sensitivity setting is about 2 cm H 2 O below the PEEP level (first and
second breaths).
mandatory breaths are set unless the sensitivity is set so low that the patient cannot
reach the threshold level, which is contraindicated. Inspiratory efforts required to
initiate a breath should be supported by an appropriate sensitivity setting.
The PEEP for the pressure-time waveforms is 10 cm H O, and since there was
2
no change in static compliance, the PIP was increased by 10 cm H O as well, when
2
compared to Figure 11-6. For the assist breaths, it can be seen that pressure drops to
8 or 2 cm H O below PEEP level to trigger the first two breaths because sensitivity is
2
set at 22 cm H O below baseline pressure, which is known as PEEP compensation.
2
Mathematical Analysis of Constant-Flow
Ventilation
For better comprehension of the waveforms during mechanical ventilation,
respiratory care practitioners (RCPs) should be able to analyze waveforms mathe-
matically to understand the principles involved. Figure 11-4 shows that once peak
P ALV for the pressure waveform is known, the P can be delineated into the P and
AO
TA
P ALV that develops throughout inspiration. Clinicians should be able to demonstrate
mathematically that given a constant flow, the P ALV and P should rise linearly in
AO
parallel and that the P remains constant. Given no change in lung-thorax compli-
TA
ance (C ), a straight line drawn from zero pressure at the beginning of inspiration to
LT
the peak P ALV at the beginning of the set pause pressure should closely predict the rise
in P ALV throughout inspiration during constant-flow, volume-controlled ventilation.
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.