Page 380 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 380
3-3
87.
3-3
g
g
q
xd
q
87.
q
e 3
p
A
p
t
p
56
e 3
56
A
56
6 A
M
6 A
2:1
2:1
Pa
g
Pa
M
Pa
1
/30
/30
6
xd
6
1
1
/09
/09
/09
t
LWB
LWB
LWBK340-c16_ pp333-387.qxd 6/30/09 12:16 AM Page 356 Aptara Inc.
c.
c.
16_
K34
K34
0-c
16_
0-c
In
a
ara
p
p
33
33
ara
a
In
356 P A R T III / Assessment of Heart Disease
A
B
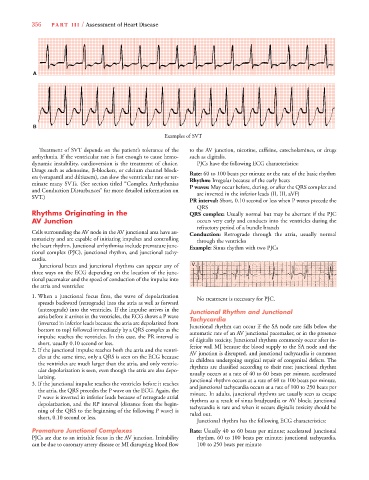
Examples of SVT
Treatment of SVT depends on the patient’s tolerance of the to the AV junction, nicotine, caffeine, catecholamines, or drugs
arrhythmia. If the ventricular rate is fast enough to cause hemo- such as digitalis.
dynamic instability, cardioversion is the treatment of choice. PJCs have the following ECG characteristics:
Drugs such as adenosine, -blockers, or calcium channel block- Rate: 60 to 100 beats per minute or the rate of the basic rhythm
ers (verapamil and diltiazem), can slow the ventricular rate or ter- Rhythm: Irregular because of the early beats
minate many SVTs. (See section titled “Complex Arrhythmias P waves: May occur before, during, or after the QRS complex and
and Conduction Disturbances” for more detailed information on are inverted in the inferior leads (II, III, aVF)
SVT.)
PR interval: Short, 0.10 second or less when P waves precede the
QRS
Rhythms Originating in the QRS complex: Usually normal but may be aberrant if the PJC
AV Junction occurs very early and conducts into the ventricles during the
refractory period of a bundle branch
Cells surrounding the AV node in the AV junctional area have au- Conduction: Retrograde through the atria, usually normal
tomaticity and are capable of initiating impulses and controlling through the ventricles
the heart rhythm. Junctional arrhythmias include premature junc- Example: Sinus rhythm with two PJCs
tional complex (PJC), junctional rhythm, and junctional tachy-
cardia.
Junctional beats and junctional rhythms can appear any of V 1
three ways on the ECG depending on the location of the junc-
tional pacemaker and the speed of conduction of the impulse into
the atria and ventricles:
1. When a junctional focus fires, the wave of depolarization No treatment is necessary for PJC.
spreads backward (retrograde) into the atria as well as forward
(anterograde) into the ventricles. If the impulse arrives in the Junctional Rhythm and Junctional
atria before it arrives in the ventricles, the ECG shows a P wave Tachycardia
(inverted in inferior leads because the atria are depolarized from Junctional rhythm can occur if the SA node rate falls below the
bottom to top) followed immediately by a QRS complex as the automatic rate of an AV junctional pacemaker, or in the presence
impulse reaches the ventricles. In this case, the PR interval is of digitalis toxicity. Junctional rhythms commonly occur after in-
short, usually 0.10 second or less. ferior wall MI because the blood supply to the SA node and the
2. If the junctional impulse reaches both the atria and the ventri- AV junction is disrupted, and junctional tachycardia is common
cles at the same time, only a QRS is seen on the ECG because in children undergoing surgical repair of congenital defects. The
the ventricles are much larger than the atria, and only ventric- rhythms are classified according to their rate; junctional rhythm
ular depolarization is seen, even though the atria are also depo- usually occurs at a rate of 40 to 60 beats per minute, accelerated
larizing. junctional rhythm occurs at a rate of 60 to 100 beats per minute,
3. If the junctional impulse reaches the ventricles before it reaches and junctional tachycardia occurs at a rate of 100 to 250 beats per
the atria, the QRS precedes the P wave on the ECG. Again, the minute. In adults, junctional rhythms are usually seen as escape
P wave is inverted in inferior leads because of retrograde atrial rhythms as a result of sinus bradycardia or AV block; junctional
depolarization, and the RP interval (distance from the begin- tachycardia is rare and when it occurs digitalis toxicity should be
ning of the QRS to the beginning of the following P wave) is ruled out.
short, 0.10 second or less.
Junctional rhythm has the following ECG characteristics:
Premature Junctional Complexes Rate: Usually 40 to 60 beats per minute; accelerated junctional
PJCs are due to an irritable focus in the AV junction. Irritability rhythm, 60 to 100 beats per minute; junctional tachycardia,
can be due to coronary artery disease or MI disrupting blood flow 100 to 250 beats per minute