Page 383 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 383
1
1
2:1
/09
/09
1
M
M
Pa
2:1
6 A
6 A
/09
q
q
q
3-3
87.
87.
6
/30
/30
xd
xd
6
t
ara
ara
p
p
t
In
c.
c.
a
a
In
p
g
g
e 3
Pa
Pa
g
59
A
A
e 3
59
59
3-3
LWB
LWBK340-c16_
33
33
K34
LWB K34 0-c 16_ p p pp333-387.qxd 6/30/09 12:16 AM Page 359 Aptara Inc.
16_
0-c
C HAPTER 1 6 / Arrhythmias and Conduction Disturbances 359
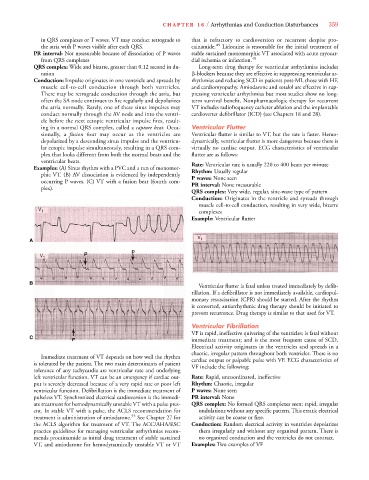
in QRS complexes or T waves. VT may conduct retrograde to that is refractory to cardioversion or recurrent despite pro-
the atria with P waves visible after each QRS. cainamide. 49 Lidocaine is reasonable for the initial treatment of
PR interval: Not measurable because of dissociation of P waves stable sustained monomorphic VT associated with acute myocar-
from QRS complexes dial ischemia or infarction. 49
QRS complex: Wide and bizarre, greater than 0.12 second in du- Long-term drug therapy for ventricular arrhythmias includes
ration -blockers because they are effective in suppressing ventricular ar-
Conduction: Impulse originates in one ventricle and spreads by rhythmias and reducing SCD in patients post-MI, those with HF,
muscle cell-to-cell conduction through both ventricles. and cardiomyopathy. Amiodarone and sotalol are effective in sup-
There may be retrograde conduction through the atria, but pressing ventricular arrhythmias but most studies show no long-
often the SA node continues to fire regularly and depolarizes term survival benefit. Nonpharmacologic therapy for recurrent
the atria normally. Rarely, one of these sinus impulses may VT includes radiofrequency catheter ablation and the implantable
conduct normally through the AV node and into the ventri- cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) (see Chapters 18 and 28).
cle before the next ectopic ventricular impulse fires, result-
ing in a normal QRS complex, called a capture beat. Occa- Ventricular Flutter
sionally, a fusion beat may occur as the ventricles are Ventricular flutter is similar to VT, but the rate is faster. Hemo-
depolarized by a descending sinus impulse and the ventricu- dynamically, ventricular flutter is more dangerous because there is
lar ectopic impulse simultaneously, resulting in a QRS com- virtually no cardiac output. ECG characteristics of ventricular
plex that looks different from both the normal beats and the flutter are as follows:
ventricular beats. Rate: Ventricular rate is usually 220 to 400 beats per minute
Examples: (A) Sinus rhythm with a PVC and a run of monomor- Rhythm: Usually regular
phic VT. (B) AV dissociation is evidenced by independently P waves: None seen
occurring P waves. (C) VT with a fusion beat (fourth com- PR interval: None measurable
plex).
QRS complex: Very wide, regular, sine-wave type of pattern
Conduction: Originates in the ventricle and spreads through
muscle cell-to-cell conduction, resulting in very wide, bizarre
V 1 complexes
Example: Ventricular flutter
V
A 1
V 1
B
Ventricular flutter is fatal unless treated immediately by defib-
rillation. If a defibrillator is not immediately available, cardiopul-
monary resuscitation (CPR) should be started. After the rhythm
is converted, antiarrhythmic drug therapy should be initiated to
prevent recurrence. Drug therapy is similar to that used for VT.
Ventricular Fibrillation
VF is rapid, ineffective quivering of the ventricles; is fatal without
C
immediate treatment; and is the most frequent cause of SCD.
Electrical activity originates in the ventricles and spreads in a
chaotic, irregular pattern throughout both ventricles. There is no
Immediate treatment of VT depends on how well the rhythm cardiac output or palpable pulse with VF. ECG characteristics of
is tolerated by the patient. The two main determinants of patient VF include the following:
tolerance of any tachycardia are ventricular rate and underlying
left ventricular function. VT can be an emergency if cardiac out- Rate: Rapid, uncoordinated, ineffective
put is severely decreased because of a very rapid rate or poor left Rhythm: Chaotic, irregular
ventricular function. Defibrillation is the immediate treatment of P waves: None seen
pulseless VT. Synchronized electrical cardioversion is the immedi- PR interval: None
ate treatment for hemodynamically unstable VT with a pulse pres- QRS complex: No formed QRS complexes seen; rapid, irregular
ent. In stable VT with a pulse, the ACLS recommendation for undulations without any specific pattern. This erratic electrical
treatment is administration of amiodarone. 53 See Chapter 27 for activity can be coarse or fine.
the ACLS algorithm for treatment of VT. The ACC/AHA/ESC Conduction: Random electrical activity in ventricles depolarizes
practice guidelines for managing ventricular arrhythmias recom- them irregularly and without any organized pattern. There is
mends procainamide as initial drug treatment of stable sustained no organized conduction and the ventricles do not contract.
VT, and amiodarone for hemodynamically unstable VT or VT Examples: Two examples of VF