Page 902 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 902
Chapter 56 Conventional and Molecular Cytogenomic Basis of Hematologic Malignancies 785
1 2 3 4 5
6 7 8 9 10 11 12
13 14 15 16 17 18
A 19 20 21 22 X Y
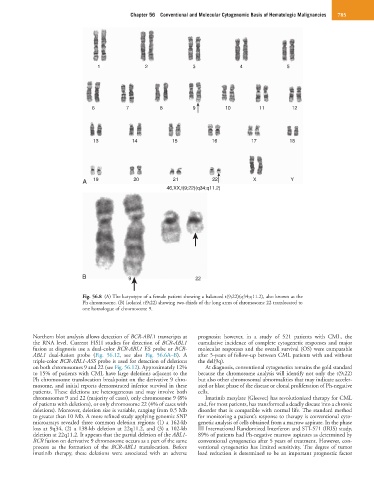
46,XX,t(9;22)(q34;q11.2)
B 9 22
Fig. 56.8 (A) The karyotype of a female patient showing a balanced t(9;22)(q34;q11.2), also known as the
Ph chromosome. (B) Isolated t(9;22) showing two-thirds of the long arms of chromosome 22 translocated to
one homologue of chromosome 9.
Northern blot analysis allows detection of BCR-ABL1 transcripts at prognosis; however, in a study of 521 patients with CML, the
the RNA level. Current FISH studies for detection of BCR-ABL1 cumulative incidence of complete cytogenetic responses and major
fusion at diagnosis use a dual-color BCR-ABL1 ES probe or BCR- molecular responses and the overall survival (OS) were comparable
ABL1 dual-fusion probe (Fig. 56.12, see also Fig. 56.6A–B). A after 5-years of follow-up between CML patients with and without
triple-color BCR-ABL1-ASS probe is used for detection of deletions the del(9q).
on both chromosomes 9 and 22 (see Fig. 56.12). Approximately 12% At diagnosis, conventional cytogenetics remains the gold standard
to 15% of patients with CML have large deletions adjacent to the because the chromosome analysis will identify not only the t(9;22)
Ph chromosome translocation breakpoint on the derivative 9 chro- but also other chromosomal abnormalities that may indicate acceler-
mosome, and initial reports demonstrated inferior survival in these ated or blast phase of the disease or clonal proliferation of Ph-negative
patients. These deletions are heterogeneous and may involve both cells.
chromosomes 9 and 22 (majority of cases), only chromosome 9 (8% Imatinib mesylate (Gleevec) has revolutionized therapy for CML
of patients with deletions), or only chromosome 22 (4% of cases with and, for most patients, has transformed a deadly disease into a chronic
deletions). Moreover, deletion size is variable, ranging from 0.5 Mb disorder that is compatible with normal life. The standard method
to greater than 10 Mb. A more refined study applying genomic SNP for monitoring a patient’s response to therapy is conventional cyto-
microarrays revealed three common deletion regions: (1) a 162-kb genetic analysis of cells obtained from a marrow aspirate. In the phase
loss at 9q34, (2) a 138-kb deletion at 22q11.2, and (3) a 102-kb III International Randomized Interferon and STI-571 (IRIS) study,
deletion at 22q11.2. It appears that the partial deletion of the ABL1- 89% of patients had Ph-negative marrow aspirates as determined by
BCR fusion on derivative 9 chromosome occurs as a part of the same conventional cytogenetics after 5 years of treatment. However, con-
process as the formation of the BCR-ABL1 translocation. Before ventional cytogenetics has limited sensitivity. The degree of tumor
imatinib therapy, these deletions were associated with an adverse load reduction is determined to be an important prognostic factor