Page 905 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 905
788 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
A
B B
C
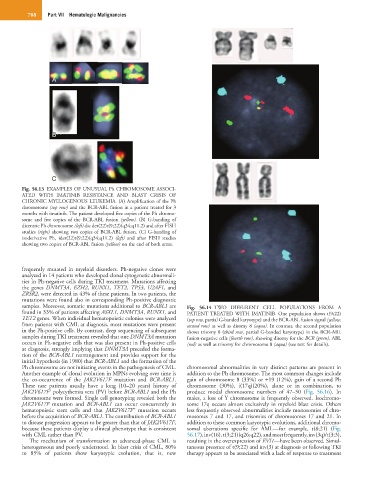
Fig. 56.13 EXAMPLES OF UNUSUAL Ph CHROMOSOME ASSOCI-
ATED WITH IMATINIB RESISTANCE AND BLAST CRISIS OF
CHRONIC MYELOGENOUS LEUKEMIA. (A) Amplification of the Ph
chromosome (top row) and the BCR-ABL fusion in a patient treated for 3
months with imatinib. The patient developed five copies of the Ph chromo-
some and five copies of the BCR-ABL fusion (yellow). (B) G-banding of
dicentric Ph chromosome (left) dic der(22)t(9;22)(q34;q11.2) and after FISH
studies (right) showing two copies of BCR-ABL fusion. (C) G-banding of
isoderivative Ph, ider(22)t(9;22)(q34;q11.2) (left) and after FISH studies
showing two copies of BCR-ABL fusion (yellow) on the end of both arms.
frequently mutated in myeloid disorders. Ph-negative clones were
analyzed in 14 patients who developed clonal cytogenetic abnormali-
ties in Ph-negative cells during TKI treatment. Mutations affecting
the genes DNMT3A, EZH2, RUNX1, TET2, TP53, U2AF1, and
ZRSR2, were detected in 43% of these patients. In two patients, the
mutations were found also in corresponding Ph-positive diagnostic
samples. Moreover, somatic mutations additional to BCR-ABL1 are Fig. 56.14 TWO DIFFERENT CELL POPULATIONS FROM A
found in 33% of patients affecting ASXL1, DNMT3A, RUNX1, and PATIENT TREATED WITH IMATINIB. One population shows t(9;22)
TET2 genes. When individual hematopoietic colonies were analyzed (top row, partial G-banded karyotype) and the BCR-ABL fusion signal (yellow,
from patients with CML at diagnosis, most mutations were present second row) as well as disomy 8 (aqua). In contrast, the second population
in the Ph-positive cells. By contrast, deep sequencing of subsequent shows trisomy 8 (third row, partial G-banded karyotype) in the BCR-ABL
samples during TKI treatment revealed that one DNMT3A mutation fusion-negative cells (fourth row), showing disomy for the BCR (green), ABL
occurs in Ph-negative cells that was also present in Ph-positive cells (red) as well as trisomy for chromosome 8 (aqua) (see text for details).
at diagnosis, strongly implying that DNMT3A preceded the forma-
tion of the BCR-ABL1 rearrangement and provides support for the
initial hypothesis (in 1980) that BCR-ABL1 and the formation of the
Ph chromosome are not initiating events in the pathogenesis of CML. chromosomal abnormalities in very distinct patterns are present in
Another example of clonal evolution in MPNs evolving over time is addition to the Ph chromosome. The most common changes include
the co-occurrence of the JAK2V617F mutation and BCR-ABL1. gain of chromosome 8 (33%) or +19 (12%), gain of a second Ph
These rare patients usually have a long (10–20 years) history of chromosome (30%), i(17q)(20%), alone or in combination, to
+
JAK2V617F polycythemia vera (PV) before BCR-ABL1 and the Ph produce modal chromosome numbers of 47–50 (Fig. 56.16). In
chromosome were formed. Single cell genotyping revealed both the males, a loss of Y chromosome is frequently observed. Isochromo-
JAK2V617F mutation and BCR-ABL1 can occur concurrently in some 17q occurs almost exclusively in myeloid blast crisis. Others
+
hematopoietic stem cells and that JAK2V617F mutation occurs less frequently observed abnormalities include monosomies of chro-
before the acquisition of BCR-ABL1. The contribution of BCR-ABL1 mosomes 7 and 17, and trisomies of chromosomes 17 and 21. In
to disease progression appears to be greater than that of JAK2V617F, addition to these common karyotypic evolutions, additional chromo-
because these patients display a clinical phenotype that is consistent somal aberrations specific for AML—for example, t(8;21) (Fig.
with CML rather than PV. 56.17), inv(16), t(3;21)(q26;q22), and most frequently, inv(3q)/t(3;3),
The mechanism of transformation to advanced-phase CML is resulting in the overexpression of EVI1—have been observed. Simul-
heterogeneous and poorly understood. In blast crisis of CML, 80% taneous presence of t(9;22) and inv(3) at diagnosis or following TKI
to 85% of patients show karyotypic evolution, that is, new therapy appears to be associated with a lack of response to treatment