Page 909 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 909
792 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
A
Fig. 56.19 BONE MARROW INTERPHASE NUCLEI AFTER FISH
B 8 22 STUDIES USING TRICOLOR PROBE FOR CHROMOSOME 4,
BAND REGION q12. The green color covers an approximately 750-kb
region centromeric from FIP1L1. The red probe is telomeric of the FIP1L1
gene. The aqua color probe begins between exons 15 and 16 of the PDGFRA
gene and extends toward the 4q telomere. In normal nuclei, as shown here,
the probe appears as two tricolor fusions because of close proximity of probes
in interphase DNA. Patients with hypereosinophilic syndrome have fusion of
FIP1L1 and PDGFRA genes by interstitial deletion and produce one signal
with green-aqua fusion and a missing orange signal. If the translocation
involves the PDGFRA gene with loci on other chromosomes, the expected
signal pattern is one orange–green fusion and one separate aqua signal.
Genetic Testing for Ph-Negative Myeloproliferative Neoplasms
At diagnosis, perform a real-time alleles-specific polymerase chain
reaction for JAK2V617F, as well as mutational studies for CALR and
MPL. Cytogenetic analysis of marrow cells is recommended for patients
with essential thrombocytopenia and polycythemia vera. Unstimulated
peripheral blood can be used instead of marrow aspirate for patients
with primary myelofibrosis. Perform FISH studies with BCR-ABL1 for
patients with thrombocythemia to exclude the diagnosis of chronic
myelogenous leukemia. FISH studies can be performed when cytoge-
netics is uninformative for detection of the most frequent abnormalities:
+8, +9, +9p, del(13)(q14), and del(20)(q11q13). A panel of five probes
includes CEP9, CDKN2A/B at 9p21, D8Z2 as a centromeric probe for
C chromosome 8, RB1 for deletion 13q, and D20S108 for deletion of
20q12. For diagnostic purpose and to monitor treatment response in
patients with hypereosinophilic syndrome, perform FISH using triple-
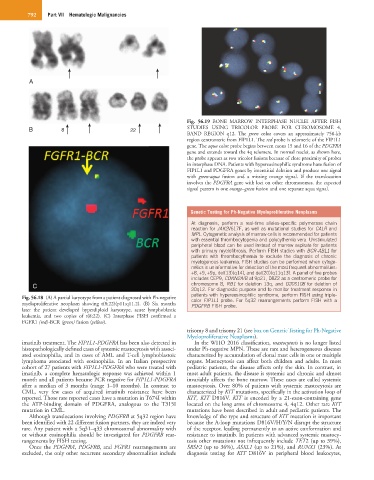
Fig. 56.18 (A) A partial karyotype from a patient diagnosed with Ph-negative color FIP1L1 probe. For 5q32 rearrangements perform FISH with a
myeloproliferative neoplasm showing t(8;22)(p11;q11.2). (B) Six months PDGFRB FISH probe.
later the patient developed hyperdiploid karyotype, acute lymphoblastic
leukemia, and two copies of t(8;22). (C) Interphase FISH confirmed a
FGFR1 (red)-BCR (green) fusion (yellow).
trisomy 8 and trisomy 21 (see box on Genetic Testing for Ph-Negative
Myeloproliferative Neoplasms).
imatinib treatment. The FIP1L1-PDGFRA has been also detected in In the WHO 2016 classification, mastocytosis is no longer listed
histopathologically defined cases of systemic mastocytosis with associ- under Ph-negative MPN. These are rare and heterogeneous diseases
ated eosinophilia, and in cases of AML and T-cell lymphoblastoic characterized by accumulation of clonal mast cells in one or multiple
lymphoma associated with eosinophilia. In an Italian prospective organs. Mastocytosis can affect both children and adults. In most
cohort of 27 patients with FIP1L1-PDGFRA who were treated with pediatric patients, the disease affects only the skin. In contrast, in
imatinib, a complete hematologic response was achieved within 1 most adult patients, the disease is systemic and chronic and almost
month and all patients became PCR negative for FIP1L1-PDGFRA invariably affects the bone marrow. These cases are called systemic
after a median of 3 months (range 1–10 months). In contrast to mastocytosis. Over 80% of patients with systemic mastocytosis are
CML, very few cases of acquired imatinib resistance have been characterized by KIT mutations, specifically in the activation loop of
reported. Those rare reported cases have a mutation in T674I within KIT, KIT D816V. KIT is encoded by a 21-exon-containing gene
the ATP-binding domain of PDGFRA, analogous to the T315I located on the long arms of chromosome 4, 4q12. Other rare KIT
mutation in CML. mutations have been described in adult and pediatric patients. The
Although translocations involving PDGFRB at 5q32 region have knowledge of the type and structure of KIT mutation is important
been identified with 22 different fusion partners, they are indeed very because the A-loop mutations D816V/H/Y/N disrupt the structure
rare. Any patient with a 5q31–q33 chromosomal abnormality with of the receptor, leading permanently to an active conformation and
or without eosinophilia should be investigated for PDGFRB rear- resistance to imatinib. In patients with advanced systemic mastocy-
rangements by FISH testing. tosis other mutations not infrequently include TET2 (up to 39%),
Once the PDGFRA, PDGFRB, and FGFR1 rearrangements are SRSF2 (up to 36%), ASXL1 (up to 21%), and RUNX1 (23%). At
excluded, the only other recurrent secondary abnormalities include diagnosis testing for KIT D816V in peripheral blood leukocytes,