Page 919 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 919
802 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
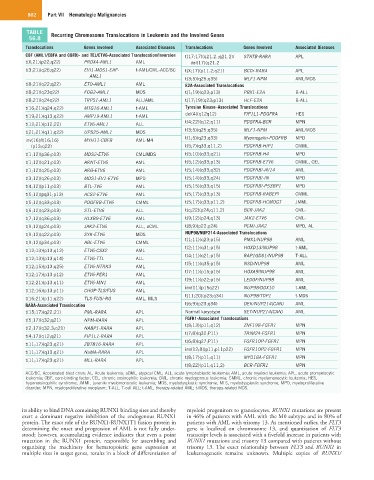
TABLE Recurring Chromosome Translocations in Leukemia and the Involved Genes
56.8
Translocations Genes Involved Associated Diseases Translocations Genes Involved Associated Diseases
CBF (AML1/CBFA and CBFB)- and TEL/ETV6-Associated Translocation/Inversion t(17;17)(q21.2.;q21.2)/ STATB-RARA APL
t(X;21)(p22;q22) PRDX4-AML1 AML del(17)(q21.2
t(3;21)(q26;q22) EVI1-MDS1-EAP- t-AML/CML-ACC/BC t(X;17)(p11.2;q21) BCOr-RARA APL
AML1
t(3;5)(q25;q35) MLF1-NPM AML/MDS
t(8;21)(q22;q22) ETO-AML1 AML E2A-Associated Translocations
t(8;21)(q23q22) FOG2-AML1 MDS t(1;19)(q23;p13) PBX1-E2A B-ALL
t(8;21)(q24q22) TRPS1-AML1 ALL/AML t(17;19)(q23;p13) HLF-E2A B-ALL
t(16;21)(q24;q22) MTG16-AML1 t-AML Tyrosine Kinase–Associated Translocations
del(4)(q12q12) FIP1L1-PDGFRA HES
t(19;21)(q13;q22) AMP19-AML1 t-AML
t(4;22)(q12;q11) PDGFRA-BCR MPN
t(12;21)(p12;22) ETV6-AML1 ALL
t(3;5)(q25;q35) MLF1-NPM AML/MDS
t(21;21)(q11;q22) UPS25-AML1 MDS
inv(16)/t(16;16) MYH11-CBFB AML-M4 t(1;5)(q23;q33) Myomegalin-PDGFRB MPD
(p13;q22) t(5;7)(q33;q11.2) PDGFRB-HIP1 CMML
t(1;12)(p36;p13) MDS2-ETV6 CML/MDS t(5:10)(q33;q21) PDGFRB-H4 MPD
t(1;12)(q21;p13) ARNT-ETV6 AML t(5;12)(q33;p13) PDGFRB-ETV6 CMML, CEL
t(1;12)(q25;p13) ARG-ETV6 AML t(5;14)(q33;q32) PDGFRB/-AV14 AML
t(3;12)(q26;p13) MDS1-EV1-ETV6 MPD t(5;14)(q33;q24) PDGFRB/-IN MPD
t(4;12)(p11;p13) BTL-TV6 AML t(5;15)(q33;q15) PDGFRB/-P53BP1 MPD
t(5;12)(pq31;p13) ACS2-ETV6 AML t(5;17)(q33;p13) PDGFRB-RABEPI CMML
t(5;12)(q33;p13) PDGFRB-ETV6 CMML t(5;17)(q33;p11.2) PDGFRB-HCMOGT JMML
t(6;12)(q23;p13) STL-ETV6 ALL t(q;22)(p24;q11.2) BCR-JAK2 CML-
t(7;12)(q36;p13) HLXB9-ETV6 AML t(9;12)(p24;q13) JAK2-ETV6 CML-
t(9;12)(p24;p13) JAK2-ETV6 ALL, aCML t(8;9)(p22;p24) PCMI-JAK2 MPD, AL
t(9;12)(q22;p13) SYK-ETV6 MDS NUP98/NUP214-Associated Translocations
t(1;11)(q23;p15) PMX1/NUP98 AML
t(9;12)(p34;p13) ABL-ETV6 CMML
t(2;11)(q31;p15) HOXD13/NUP98 t-AML
t(12;13)(p13;q12) ETV6-CSX2 AML
t(4;11)(q21;p15) RAP1GDS1/NUP98 T-ALL
t(12;13)(p13;q14) ETV6-TTL ALL
t(5;11)(q35;p15) NSD/NUP98 AML
t(12;15)(p13;q25) ETV6-NTRK3 AML
t(7:11)(p15;p15) HOXA9/NUP98 AML
t(12;17)(p13;p12) ETV6-PER1 AML
t(9;11)(p22;p15) LEDGF/NUP98 AML
t(12;21)(p13;q11) ETV6-MN1 AML
inv(11)(p15q22) NUP98/DDX10 t-AML
t(12;16)(p13;p11) CHOP-TLS/FUS AML
t(11;20)(p23;q34) NUP98/TOP1 t-MDS
t(16;21)(p11;q22) TLS-FUS/-RG AML, MLS
RARA-Associated Translocation t(6;9)(p23;q34) DEK/NUP214(CAN) AML
t(15;17)(q22;21) PML-RARA APL Normal karyotype SET/NUP214(CAN) AML
t(5;17)(q32;q21) NPM-RARA APL FGFR1-Associated Translocations
t(8;13)(p11;q12) ZNF198-FGFR1 MPN
t(2;17)(q32.3;q21) NABP1-RARA APL
t(7;8)(q32;P11) TRIM24-FGFR1 MPN
t(4;17)(q12;q21) FIP1L1-RARA APL
t(6;8)(q27;P11) FGFR1OP-FGFR1 MPN
t(11;17)(q23;q21) ZBTB16-RARA APL
ins(12;8)(p11;p11p22) FGFR1OP2-FGFR1 MPN
t(11;17)(q13;q21) NuMA-RARA APL
t(8;17)(p11;q11) MYO18A-FGFR1 MPN
t(11;17)(q23;q21) MLL-RARA APL
t(8;22)(p11;q11,2) BCR-FGFR1 MPN
ACC/BC, Accelerated blast crisis; AL, Acute leukemia; aCML, atypical CML; ALL, acute lymphoblastic leukemia; AML, acute myeloid leukemia; APL, acute promyelocytic
leukemia; CBF, core-binding factor; CEL, chronic eosinophilic leukemia; CML, chronic myelogenous leukemia; CMML, chronic myelomonocytic leukemia; HES,
hypereosinophilic syndrome; JMML, juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia; MDS, myelodysplastic syndrome; MLS, myelodysplastic syndrome; MPD, myeloproliferative
disorder; MPN, myeloproliferative neoplasm; T-ALL, T-cell ALL; t-AML, therapy-related AML; t-MDS, therapy-related MDS.
its ability to bind DNA containing RUNX1 binding sites and thereby myeloid progenitors to granulocytes. RUNX1 mutations are present
exert a dominant negative inhibition of the endogenous RUNX1 in 46% of patients with AML with the M0 subtype and in 80% of
protein. The exact role of the RUNX1-RUNX1T1 fusion protein in patients with AML with trisomy 13. As mentioned earlier, the FLT3
determining the onset and progression of AML is not fully under- gene is localized on chromosome 13, and quantitation of FLT3
stood; however, accumulating evidence indicates that even a point transcript levels is associated with a fivefold increase in patients with
mutation in the RUNX1 protein, responsible for assembling and RUNX1 mutations and trisomy 13 compared with patients without
organizing the machinery for hematopoietic gene expression at trisomy 13. The exact relationship between FLT3 and RUNX1 in
multiple sites in target genes, results in a block of differentiation of leukemogenesis remains unknown. Multiple copies of RUNX1/