Page 962 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 962
Chapter 56 Conventional and Molecular Cytogenomic Basis of Hematologic Malignancies 845
TABLE Genetic Rearrangements in T-ALL—cont’d
56.18
Genetic Lesion Gene Frequency % Outcome
Activating mutation NRAS 5 no imact
Activating mutation KRAS 2 NA
Activating mutation JAK1 4–18 no imact
t(9;12)(p24;p13) ETV6-JAK2 <1 no imact
Activating mutation FLT3 5–10 no imact
t(X;7)((q22;q34) IRS4 <1 NA
t(X;14)(q22;q11.2) IRS4
Inactivating mutation DNM2 15 NA
t(9;22)(q34;q11.2) BCR-ABL1 1 poor
Modified from Belver and Ferrando Nature 16: 494, 2016.
NA, Not available.
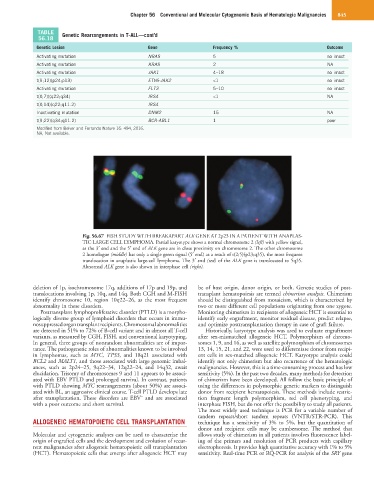
Fig. 56.67 FISH STUDY WITH BREAKAPART ALK GENE AT 2p23 IN A PATIENT WITH ANAPLAS-
TIC LARGE CELL LYMPHOMA. Partial karyotype shows a normal chromosome 2 (left) with yellow signal,
as the 3′ end and the 5′ end of ALK gene are in close proximity on chromosome 2. The other chromosome
2 homologue (middle) has only a single green signal (5′ end) as a result of t(2;5)(p23;q35), the most frequent
translocation in anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. The 3′ end (red) of the ALK gene is translocated to 5q35.
Abnormal ALK gene is also shown in interphase cell (right).
deletion of 1p, isochromosome 17q, additions of 17p and 19p, and be of host origin, donor origin, or both. Genetic studies of post-
translocations involving 1p, 10q, and 14q. Both CGH and M-FISH transplant hematopoiesis are termed chimerism analysis. Chimerism
identify chromosome 10, region 10q22–26, as the most frequent should be distinguished from mosaicism, which is characterized by
abnormality in these disorders. two or more different cell populations originating from one zygote.
Posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD) is a morpho- Monitoring chimerism in recipients of allogeneic HCT is essential to
logically diverse group of lymphoid disorders that occurs in immu- identify early engraftment, monitor residual disease, predict relapse,
nosuppressed organ transplant recipients. Chromosomal abnormalities and optimize posttransplantation therapy in case of graft failure.
are detected in 51% to 72% of B-cell variant and in almost all T-cell Historically, karyotype analysis was used to evaluate engraftment
variants, as measured by CGH, FISH, and conventional karyotyping. after sex-mismatched allogeneic HCT. Polymorphism of chromo-
In general, three groups of nonrandom abnormalities are of impor- somes 1, 9, and 16, as well as satellite polymorphism of chromosomes
tance. The pathogenetic roles of abnormalities known to be involved 13, 14, 15, 21, and 22, were used to differentiate donor from recipi-
in lymphomas, such as MYC, TP53, and 18q21 associated with ent cells in sex-matched allogeneic HCT. Karyotype analysis could
BCL2 and MALT1, and those associated with large genomic imbal- identify not only chimerism but also recurrence of the hematologic
ances, such as 2p24–25, 9q22–34, 12q22–24, and 14q32, await malignancies. However, this is a time-consuming process and has low
elucidation. Trisomy of chromosomes 9 and 11 appears to be associ- sensitivity (5%). In the past two decades, many methods for detection
ated with EBV PTLD and prolonged survival. In contrast, patients of chimerism have been developed. All follow the basic principle of
with PTLD showing MYC rearrangements (about 50%) are associ- using the differences in polymorphic genetic markers to distinguish
ated with BL, an aggressive clinical course. T-cell PTLD develops late donor from recipient hematopoiesis. These methods include restric-
−
after transplantation. These disorders are EBV and are associated tion fragment length polymorphism, red cell phenotyping, and
with a poor outcome and short survival. interphase FISH, but do not offer the possibility to study all patients.
The most widely used technique is PCR for a variable number of
tandem repeats/short tandem repeats (VNTR/STR-PCR). This
ALLOGENEIC HEMATOPOIETIC CELL TRANSPLANTATION technique has a sensitivity of 3% to 5%, but the quantitation of
donor and recipient cells may be cumbersome. The method that
Molecular and cytogenetic analyses can be used to characterize the allows study of chimerism in all patients involves fluorescence label-
origin of engrafted cells and the development and evolution of recur- ing of the primers and resolution of PCR products with capillary
rent malignancies after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation electrophoresis. It provides high quantitative accuracy with 1% to 5%
(HCT). Hematopoietic cells that emerge after allogeneic HCT may sensitivity. Real-time PCR or RQ-PCR for analysis of the SRY gene