Page 1768 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1768
1742 Part XI: Malignant Lymphoid Diseases Chapter 107: Myeloma 1743
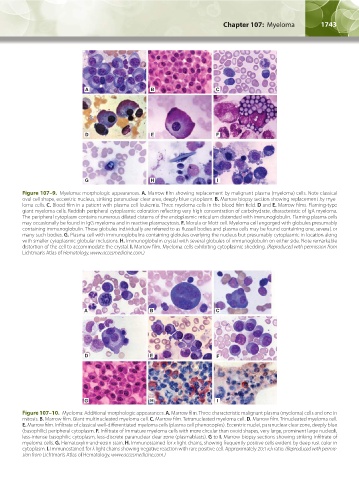
A B C
D E F
G H I
Figure 107–9. Myeloma: morphologic appearances. A. Marrow film showing replacement by malignant plasma (myeloma) cells. Note classical
oval cell shape, eccentric nucleus, striking paranuclear clear area, deeply blue cytoplasm. B. Marrow biopsy section showing replacement by mye-
loma cells. C. Blood film in a patient with plasma cell leukemia. Three myeloma cells in the blood film field. D and E. Marrow films. Flaming-type
giant myeloma cells. Reddish peripheral cytoplasmic coloration reflecting very high concentration of carbohydrate, characteristic of IgA myeloma.
The peripheral cytoplasm contains numerous dilated cisterns of the endoplasmic reticulum distended with immunoglobulin. Flaming plasma cells
may occasionally be found in IgG myeloma and in reactive plasmacytosis. F. Morula or Mott cell. Myeloma cell engorged with globules presumably
containing immunoglobulin. These globules individually are referred to as Russell bodies and plasma cells may be found containing one, several, or
many such bodies. G. Plasma cell with immunoglobulins containing globules overlying the nucleus but presumably cytoplasmic in location along
with smaller cytoplasmic globular inclusions. H. Immunoglobulin crystal with several globules of immunoglobulin on either side. Note remarkable
distortion of the cell to accommodate the crystal. I. Marrow film. Myeloma cells exhibiting cytoplasmic shedding. (Reproduced with permission from
Lichtman’s Atlas of Hematology, www.accesmedicine.com.)
A B C
D E F
G H I
Figure 107–10. Myeloma: Additional morphologic appearances. A. Marrow film. Three characteristic malignant plasma (myeloma) cells and one in
mitosis. B. Marrow film. Giant multinucleated myeloma cell. C. Marrow film. Tetranucleated myeloma cell. D. Marrow film. Trinucleated myeloma cell.
E. Marrow film. Infiltrate of classical well-differentiated myeloma cells (plasma cell phenocopies). Eccentric nuclei, paranuclear clear zone, deeply blue
(basophilic) peripheral cytoplasm. F. Infiltrate of immature myeloma cells with more circular than ovoid shapes, very large, prominent large nucleoli,
less-intense basophilic cytoplasm, less-discrete paranuclear clear zone (plasmablasts). G to I. Marrow biopsy sections showing striking infiltrate of
myeloma cells. G. Hematoxylin-and-eosin stain. H. Immunostained for κ light chains, showing frequently positive cells evident by deep rust color in
cytoplasm. I. Immunostained for λ light chains showing negative reaction with rare positive cell. Approximately 20:1 κ:λ ratio. (Reproduced with permis-
sion from Lichtman’s Atlas of Hematology, www.accesmedicine.com.)
Kaushansky_chapter 107_p1733-1772.indd 1743 9/21/15 12:34 PM