Page 1770 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1770
1744 Part XI: Malignant Lymphoid Diseases Chapter 107: Myeloma 1745
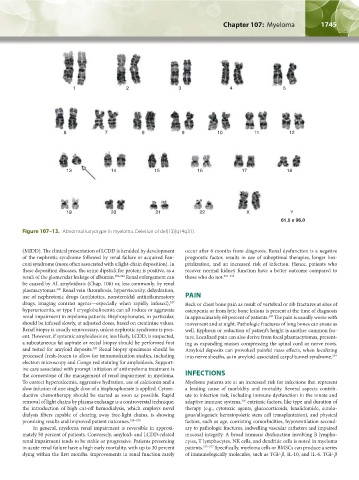
1 2 3 4 5
6 7 8 9 10 11 12
13 14 15 16 17 18
19 20 21 22 X Y
61.0 x 96.0
Figure 107–13. Abnormal karyotype in myeloma. Deletion of del(13)(q14q31).
(MIDD). The clinical presentation of LCDD is heralded by development occur after 6 months from diagnosis. Renal dysfunction is a negative
of the nephrotic syndrome followed by renal failure or acquired Fan- prognostic factor, results in use of suboptimal therapies, longer hos-
coni syndrome (more often associated with κ light-chain deposition). In pitalization, and an increased risk of infection. Hence, patients who
these deposition diseases, the urine dipstick for protein is positive, as a recover normal kidney function have a better outcome compared to
result of the glomerular leakage of albumin. 256,324 Renal enlargement can those who do not. 331–333
be caused by AL amyloidosis (Chap. 108) or, less commonly, by renal
plasmacytomas. Renal vein thrombosis, hyperviscosity, dehydration,
326
use of nephrotoxic drugs (antibiotics, nonsteroidal antiinflammatory PAIN
drugs, imaging contrast agents—especially when rapidly infused), Back or chest bone pain as result of vertebral or rib fractures at sites of
327
hyperuricemia, or type I cryoglobulinemia can all induce or aggravate osteopenia or from lytic bone lesions is present at the time of diagnosis
renal impairment in myeloma patients. Bisphosphonates, in particular, in approximately 60 percent of patients. The pain is usually worse with
247
should be infused slowly, at adjusted doses, based on creatinine values. movement and at night. Pathologic fractures of long bones can ensue as
Renal biopsy is usually unnecessary, unless nephrotic syndrome is pres- well. Kyphosis or reduction of patient’s height is another common fea-
ent. However, if systemic amyloidosis or, less likely, LCDD, is suspected, ture. Localized pain can also derive from focal plasmacytomas, present-
a subcutaneous fat aspirate or rectal biopsy should be performed first ing as expanding masses compressing the spinal cord or nerve roots.
and tested for amyloid deposits. Renal biopsy specimens should be Amyloid deposits can provoked painful mass effects, when localizing
320
processed fresh-frozen to allow for immunofixation studies, including into nerve sheaths, as in amyloid-associated carpal tunnel syndrome. 334
electron microscopy and Congo red staining for amyloidosis. Support-
ive care associated with prompt initiation of antimyeloma treatment is
the cornerstone of the management of renal impairment in myeloma. INFECTIONS
To correct hypercalcemia, aggressive hydration, use of calcitonin and a Myeloma patients are at an increased risk for infections that represent
slow infusion of one single dose of a bisphosphonate is applied. Cytore- a leading cause of morbidity and mortality. Several aspects contrib-
ductive chemotherapy should be started as soon as possible. Rapid ute to infection risk, including immune dysfunction in the innate and
removal of light chains by plasma exchange is a controversial technique; adaptive immune systems, extrinsic factors, like type and duration of
335
the introduction of high cut-off hemodialysis, which employs novel therapy (e.g., cytotoxic agents, glucocorticoids, lenalidomide, autolo-
dialysis filters capable of clearing away free-light chains, is showing gous/allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation), and physical
promising results and improved patient outcomes. 328–330 factors, such as age, coexisting comorbidities, hypoventilation second-
In general, myeloma renal impairment is reversible in approxi- ary to pathologic fractures, indwelling vascular catheters and impaired
mately 50 percent of patients. Conversely, amyloid- and LCDD-related mucosal integrity. A broad immune dysfunction involving B lympho-
renal impairment tends to be stable or progressive. Patients presenting cytes, T lymphocytes, NK cells, and dendritic cells is noted in myeloma
in acute renal failure have a high early mortality, with up to 30 percent patients. 335–337 Specifically, myeloma cells or BMSCs can produce a series
dying within the first months. Improvements in renal function rarely of immunologically molecules, such as TGF-β, IL-10, and IL-6. TGF-β
Kaushansky_chapter 107_p1733-1772.indd 1745 9/21/15 12:34 PM