Page 1383 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 1383
956 PART 8: Renal and Metabolic Disorders
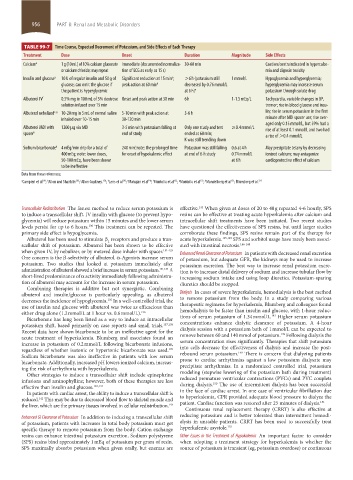
TABLE 99-7 Time Course, Expected Decrement of Potassium, and Side Effects of Each Therapy
Treatment Dose Onset Duration Magnitude Side Effects
Calcium a 1 g (10 mL) of 10% calcium gluconate Immediate (documented normaliza- 30-60 min Caution/contraindicated in hypercalce-
or calcium chloride; may repeat tion of ECG as early as 15 s) mia and digoxin toxicity
a
Insulin and glucose a 10 U of regular insulin and 50 g of Significant reduction at 15 min ; >6 h (potassium still 1 mmol/L Hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia;
glucose; can omit the glucose if peak action at 60 min d decreased by 0.76 mmol/L hyperglycemia may increase serum
the patient is hyperglycemic at 6 h) e potassium through solute drag
Albuterol IV f 0.5% mg in 100 mL of 5% dextrose Onset and peak action at 30 min 6 h 1-1.5 mEq/L Tachycardia, variable changes in BP,
solution infused over 15 min tremor; rise in blood glucose and insu-
Albuterol nebulized c, g 10-20 mg in 5 mL of normal saline 5-10 min with peak action at 3-6 h lin; rise in serum potassium in the first
inhaled over 10-15 min 30-120 min minute after MDI spacer use; rise aver-
aged only 0.15 mmol/L, but 59% had a
Albuterol MDI with 1200 µg via MDI 3-5 min with potassium falling at Only one study and test ≥0.4 mmol/L rise of at least 0.1 mmol/L and two had
spacer h end of study ended at 60 min; a rise of >0.4 mmol/L
K was still trending down
i
Sodium bicarbonate b 4 mEq/min drip for a total of 240 min;note: the prolonged time Potassium was still falling 0.6 at 4 h May precipitate tetany by decreasing
400 mEq; note: lower doses, for onset of hypokalemic effect at end of 6-h study 0.74 mmol/L ionized calcium; may antagonize
50-100 mEq, have been shown at 6 h cardioprotective effect of calcium
to be ineffective
Data from these references:
320 e
136 d
a Campieri et al ; Allon and Shanklin ; Allon Copkney. ; Lens et al ; Mahajan et al ; Montoliu et al ; Montoliu et al ; Mandelberg et al ; Blumberg et al.
319 b
130 c
140 f
132 h
131 i
321
133 g
Transcellular Redistribution The fastest method to reduce serum potassium is effective. When given at doses of 20 to 40 g repeated 4-6 hourly, SPS
144
to induce a transcellular shift. IV insulin with glucose (to prevent hypo- resins can be effective at treating acute hyperkalemia after calcium and
glycemia) will reduce potassium within 15 minutes and the lower serum intracellular shift treatments have been initiated. Two recent studies
levels persist for up to 6 hours. This treatment can be repeated. The have questioned the effectiveness of SPS resins, but until larger studies
130
primary side effect is hypoglycemia. corroborate these findings, SPS resins remain part of the therapy for
Albuterol has been used to stimulate β receptors and produce a tran- acute hyperkalemia. 125,145 SPS and sorbitol usage have rarely been associ-
2
scellular shift of potassium. Albuterol has been shown to be effective ated with intestinal necrosis. 146-148
when given IV, by nebulizer, or by metered dose inhaler with spacer. 131-133 Enhanced Renal Clearance of Potassium In patients with decreased renal excretion
One concern is the β-selectivity of albuterol. α-Agonists increase serum of potassium, but adequate GFR, the kidneys may be used to increase
potassium. Two studies that looked at potassium immediately after potassium excretion. The best way to increase renal potassium excre-
administration of albuterol showed a brief increase in serum potassium. 131,134 A tion is to increase distal delivery of sodium and increase tubular flow by
short-lived predominance of α activity immediately following administra- increasing sodium intake and using loop diuretics. Potassium-sparing
tion of albuterol may account for the increase in serum potassium. diuretics should be stopped.
Combining therapies is additive but not synergistic. Combining
albuterol and insulin/glucose is particularly appealing, as albuterol Dialysis In cases of severe hyperkalemia, hemodialysis is the best method
decreases the incidence of hypoglycemia. In a well-controlled trial, the to remove potassium from the body. In a study comparing various
135
use of insulin and glucose with albuterol was twice as efficacious than therapeutic regimens for hyperkalemia, Blumberg and colleagues found
either drug alone (1.2 mmol/L at 1 hour vs. 0.6 mmol/L). 136 hemodialysis to be faster than insulin and glucose, with 1-hour reduc-
141
Bicarbonate has long been listed as a way to induce an intracellular tions of serum potassium of 1.34 mmol/L. Higher serum potassium
potassium shift, based primarily on case reports and small trials. 137,138 concentrations enhance dialytic clearance of potassium. A 4-hour
Recent data have shown bicarbonate to be an ineffective agent for the dialysis session with a potassium bath of 1 mmol/L can be expected to
149
acute treatment of hyperkalemia. Blumberg and associates found an remove between 60 and 140 mmol of potassium. Following dialysis the
increase in potassium of 0.2 mmol/L following bicarbonate infusions, serum concentration rises significantly. Therapies that shift potassium
regardless of whether isotonic or hypertonic bicarbonate was used. into cells decrease the effectiveness of dialysis and increase the post-
139
149
Sodium bicarbonate was also ineffective in patients with low serum rebound serum potassium. There is concern that dialyzing patients
bicarbonate. Additionally, increased pH lowers ionized calcium, increas- prone to cardiac arrhythmias against a low potassium dialysate may
ing the risk of arrhythmia with hyperkalemia. precipitate arrhythmias. In a randomized controlled trial, potassium
Other strategies to induce a transcellular shift include epinephrine modeling (stepwise lowering of the potassium bath during treatment)
infusions and aminophylline; however, both of these therapies are less reduced premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) and PVC couplets
150
effective than insulin and glucose. 140,141 during dialysis. The use of intermittent dialysis has been successful
In patients with cardiac arrest, the ability to induce a transcellular shift is in the face of cardiac arrest. In one case of ventricular fibrillation due
reduced. This may be due to decreased blood flow to skeletal muscle and to hyperkalemia, CPR provided adequate blood pressure to dialyze the
142
151
the liver, which are the primary tissues involved in cellular redistribution. 143 patient. Cardiac function was restored after 25 minutes of dialysis.
Continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) is also effective at
Enhanced GI Clearance of Potassium In addition to inducing a transcellular shift reducing potassium and is better tolerated than intermittent hemodi-
of potassium, patients with increases in total body potassium must get alysis in unstable patients. CRRT has been used to successfully treat
specific therapy to remove potassium from the body. Cation exchange hyperkalemic asystole. 152
resins can enhance intestinal potassium excretion. Sodium polystyrene Other Issues in the Treatment of Hypokalemia An important factor to consider
(SPS) resins bind approximately 1 mEq of potassium per gram of resin. when adopting a treatment strategy for hyperkalemia is whether the
SPS maximally absorbs potassium when given orally, but enemas are source of potassium is transient (eg, potassium overdose) or continuous
section08.indd 956 1/14/2015 8:28:16 AM