Page 1388 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 1388
CHAPTER 99: Electrolyte Disorders in Critical Care 961
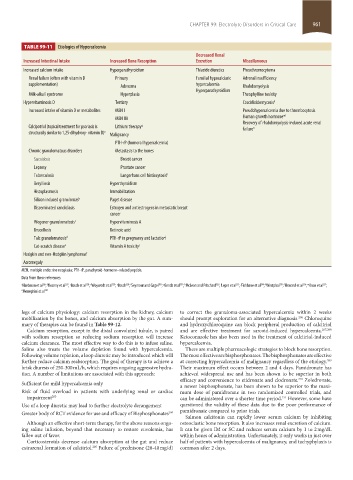
TABLE 99-11 Etiologies of Hypercalcemia
Decreased Renal
Increased Intestinal Intake Increased Bone Resorption Excretion Miscellaneous
Increased calcium intake Hyperparathyroidism Thiazide diuretics Pheochromocytoma
Renal failure (often with vitamin D Primary Familial hypocalciuric Adrenal insufficiency
supplementation) Adenoma hypercalcemia Rhabdomyolysis
Hyperparathyroidism
Milk-alkali syndrome Hyperplasia Theophylline toxicity
Hypervitaminosis D Tertiary Coccidioidomycosis k
Increased intake of vitamin D or metabolites MEN I Pseudohypercalcemia due to thrombocytosis
MEN IIA Human growth hormone ml
Recovery of rhabdomyolysis-induced acute renal
Calcipotriol (topical treatment for psoriasis is Lithium therapy g failure n
structurally similar to 1,25-dihydroxy- vitamin D) a Malignancy
PTH-rP (humoral hypercalcemia)
Chronic granulomatous disorders Metastasis to the bones
Sarcoidosis Breast cancer
Leprosy Prostate cancer
Tuberculosis Langerhans cell histiocytosis h
Berylliosis Hyperthyroidism
Histoplasmosis Immobilization
Silicon induced granulomas b Paget disease
Disseminated candidiasis Estrogen and antiestrogens in metastatic breast
cancer
Wegener granulomatosis c Hypervitaminosis A
Brucellosis Retinoic acid
Talc granulomatosis d PTH-rP in pregnancy and lactation i
Cat-scratch disease e Vitamin A toxicity j
Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphomas f
Acromegaly
MEN, multiple endocrine neoplasia; PTH-rP, parathyroid-hormone–related peptide.
Data from these references:
326 b
329 e
328 d
327 c
330 f
335 l
334 k
337
336 m
333 j
331 h
205 g
332 i
a Hardman et al ; Kozeny et al ; Bosch et al ; Woywodt et al ; Bosch ; Seymour and Gagel ; Bendz et al ; McLean and Pritchard ; Lepre et al ; Fishbane et al ; Westphal ; Howard et al ; Knox et al ;
n Meneghini et al 338
legs of calcium physiology: calcium resorption in the kidney, calcium to correct the granuloma-associated hypercalcemia within 2 weeks
mobilization by the bones, and calcium absorption by the gut. A sum- should prompt exploration for an alternative diagnosis. Chloroquine
206
mary of therapies can be found in Table 99-12. and hydroxychloroquine can block peripheral production of calcitriol
Calcium resorption, except in the distal convoluted tubule, is paired and are effective treatment for sarcoid-induced hypercalcemia. 207,208
with sodium resorption so reducing sodium resorption will increase Ketoconazole has also been used in the treatment of calcitriol-induced
calcium clearance. The most effective way to do this is to infuse saline. hypercalcemia.
Saline also treats the volume depletion found with hypercalcemia. There are multiple pharmacologic strategies to block bone resorption.
Following volume repletion, a loop diuretic may be introduced which will The most effective are bisphosphonates. The bisphosphonates are effective
further reduce calcium reabsorption. The goal of therapy is to achieve a at correcting hypercalcemia of malignancy regardless of the etiology.
209
brisk diuresis of 250-300 mL/h, which requires ongoing aggressive hydra- Their maximum effect occurs between 2 and 4 days. Pamidronate has
tion. A number of limitations are associated with this approach: achieved widespread use and has been shown to be superior in both
efficacy and convenience to etidronate and clodronate. Zoledronate,
210
Sufficient for mild hypercalcemia only a newer bisphosphonate, has been shown to be superior to the maxi-
Risk of fluid overload in patients with underlying renal or cardiac mum dose of pamidronate in two randomized controlled trials, and
impairment 203 can be administered over a shorter time period. However, some have
211
Use of a loop diuretic may lead to further electrolyte derangement questioned the validity of these data due to the poor performance of
Greater body of RCT evidence for use and efficacy of Bisphosphonates 204 pamidronate compared to prior trials.
Salmon calcitonin can rapidly lower serum calcium by inhibiting
Although an effective short-term therapy, for the above reasons ongo- osteoclastic bone resorption. It also increases renal excretion of calcium.
ing saline infusion, beyond that necessary to restore euvolemia, has It can be given IM or SC and reduces serum calcium by 1 to 2 mg/dL
fallen out of favor. within hours of administration. Unfortunately, it only works in just over
Corticosteroids decrease calcium absorption at the gut and reduce half of patients with hypercalcemia of malignancy, and tachyphylaxis is
extrarenal formation of calcitriol. Failure of prednisone (20-40 mg/d) common after 2 days.
205
section08.indd 961 1/14/2015 8:28:20 AM