Page 18 - Focus SPM KSSM F4 2020 - Chemistry
P. 18
Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 3 The Mole Concept, Chemical Formula and Equation
ACTIVITY 3.2
Aim: To determine the empirical formula of copper(II) oxide
-3
Materials: 2 mol dm sulphuric acid, 1 mol dm copper(II) sulphate solution, zinc granules, copper(II)
-3
oxide, anhydrous calcium chloride and wooden splinter.
Apparatus: Combustion tube with one hole at the end, Bunsen burner, flat-bottomed flask, thistle
funnel, stoppers, glass tube, retort stand and clamp, balance, U-tube, spatula and porcelain
dish.
Procedure:
1. The mass of the combustion tube with the porcelain dish in it is weighed.
2. One spatulaful of copper(II) oxide is added to the porcelain dish. The tube is weighed again.
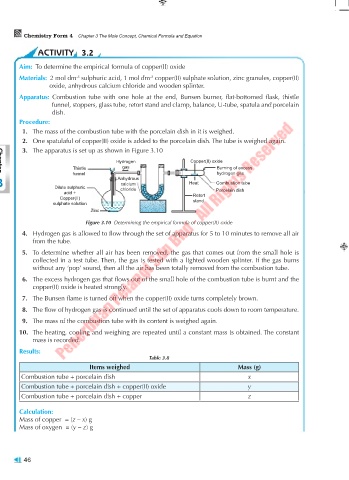
3. The apparatus is set up as shown in Figure 3.10
Hydrogen Copper(II) oxide
Thistle gas Burning of excess
funnel hydrogen gas
Chapter
3 Dilute sulphuric Anhydrous Heat Combustion tube
calcium
acid + chloride Porcelain dish
Copper(II) Retort
stand
sulphate solution
Zinc
Figure 3.10 Determining the empirical formula of copper(II) oxide
4. Hydrogen gas is allowed to flow through the set of apparatus for 5 to 10 minutes to remove all air
from the tube.
5. To determine whether all air has been removed, the gas that comes out from the small hole is
collected in a test tube. Then, the gas is tested with a lighted wooden splinter. If the gas burns
without any ‘pop’ sound, then all the air has been totally removed from the combustion tube.
6. The excess hydrogen gas that flows out of the small hole of the combustion tube is burnt and the
copper(II) oxide is heated strongly.
7. The Bunsen flame is turned off when the copper(II) oxide turns completely brown.
8. The flow of hydrogen gas is continued until the set of apparatus cools down to room temperature.
9. The mass of the combustion tube with its content is weighed again.
10. The heating, cooling and weighing are repeated until a constant mass is obtained. The constant
mass is recorded.
Results:
Table 3.8
Items weighed Mass (g)
Combustion tube + porcelain dish x
Combustion tube + porcelain dish + copper(II) oxide y
Combustion tube + porcelain dish + copper z
Calculation:
Mass of copper = (z – x) g
Mass of oxygen = (y – z) g
46
03 SPM CHEMISTRY F4.indd 46 27/02/2020 11:23 AM