Page 17 - Focus SPM KSSM F4 2020 - Chemistry
P. 17
Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 3 The Mole Concept, Chemical Formula and Equation
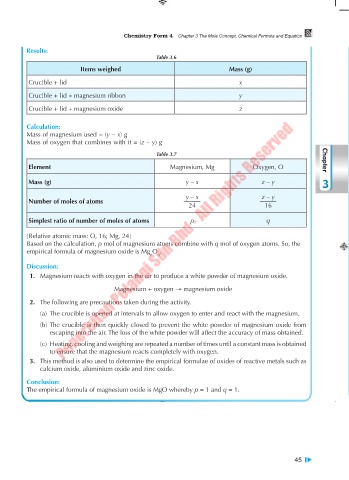
Results:
Table 3.6
Items weighed Mass (g)
Crucible + lid x
Crucible + lid + magnesium ribbon y
Crucible + lid + magnesium oxide z
Calculation:
Mass of magnesium used = (y – x) g
Mass of oxygen that combines with it = (z – y) g
Table 3.7
Element Magnesium, Mg Oxygen, O Chapter
Mass (g) y – x z – y 3
y – x z – y
Number of moles of atoms
24 16
Simplest ratio of number of moles of atoms p q
[Relative atomic mass: O, 16; Mg, 24]
Based on the calculation, p mol of magnesium atoms combine with q mol of oxygen atoms. So, the
empirical formula of magnesium oxide is Mg O .
p q
Discussion:
1. Magnesium reacts with oxygen in the air to produce a white powder of magnesium oxide.
Magnesium + oxygen → magnesium oxide
2. The following are precautions taken during the activity.
(a) The crucible is opened at intervals to allow oxygen to enter and react with the magnesium.
(b) The crucible is then quickly closed to prevent the white powder of magnesium oxide from
escaping into the air. The loss of the white powder will affect the accuracy of mass obtained.
(c) Heating, cooling and weighing are repeated a number of times until a constant mass is obtained
to ensure that the magnesium reacts completely with oxygen.
3. This method is also used to determine the empirical formulae of oxides of reactive metals such as
calcium oxide, aluminium oxide and zinc oxide.
Conclusion:
The empirical formula of magnesium oxide is MgO whereby p = 1 and q = 1.
45
03 SPM CHEMISTRY F4.indd 45 27/02/2020 11:23 AM