Page 205 - Class-11-Physics-Part-1_Neat
P. 205
GRAVITATION 191
( )
F h GM Thus the force on the point mass is
g h = E 2 . (8.14)
( ) =
m (R + h ) F (d) = G M m / (R – d ) 2 (8.17)
E s E
This is clearly less than the value of g on the Substituting for M from above , we get
s
GM E 3
surface of earth : g = 2 . For h << R ,we can F (d) = G M m ( R – d ) / R E (8.18)
E
E
R E
E and hence the acceleration due to gravity at
expand the RHS of Eq. (8.14) :
a depth d,
GM E − 2
d
g ( ) = = g (1 h R+ / E ) F ( )
h
/
R E 2 (1 h R E ) 2 g(d) = is
+
m
h
For << 1 , using binomial expression, F d
( ) GM
R E
d
E g ( ) = = 3 (R − d )
E
2 h m R E
g h ( ) ≅ g 1 − . (8.15)
R R − d
E
E
Equation (8.15) thus tells us that for small = g R = g (1 d R− / E ) (8.19)
heights h above the value of g decreases by a E
Thus, as we go down below earth’s surface,
factor (1 2 /h R− ).
E the acceleration due gravity decreases by a factor
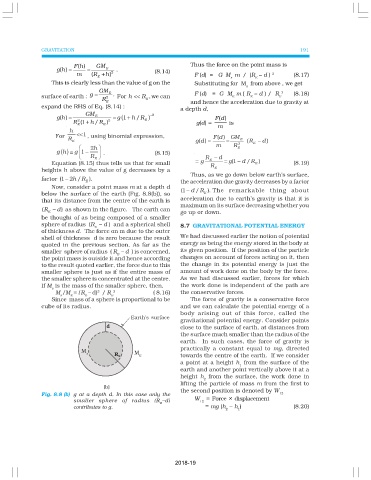
Now, consider a point mass m at a depth d
(1 d R ). The remarkable thing about
−
/
below the surface of the earth (Fig. 8.8(b)), so E
that its distance from the centre of the earth is acceleration due to earth’s gravity is that it is
maximum on its surface decreasing whether you
(R − d ) as shown in the figure. The earth can
E go up or down.
be thought of as being composed of a smaller
sphere of radius (R – d ) and a spherical shell
E 8.7 GRAVITATIONAL POTENTIAL ENERGY
of thickness d. The force on m due to the outer
shell of thickness d is zero because the result We had discussed earlier the notion of potential
quoted in the previous section. As far as the energy as being the energy stored in the body at
smaller sphere of radius ( R – d ) is concerned, its given position. If the position of the particle
E
the point mass is outside it and hence according changes on account of forces acting on it, then
to the result quoted earlier, the force due to this the change in its potential energy is just the
smaller sphere is just as if the entire mass of amount of work done on the body by the force.
the smaller sphere is concentrated at the centre. As we had discussed earlier, forces for which
If M is the mass of the smaller sphere, then, the work done is independent of the path are
s
3
M /M = ( R – d) / R 3 ( 8.16) the conservative forces.
s E E E
Since mass of a sphere is proportional to be The force of gravity is a conservative force
cube of its radius. and we can calculate the potential energy of a
body arising out of this force, called the
gravitational potential energy. Consider points
close to the surface of earth, at distances from
the surface much smaller than the radius of the
earth. In such cases, the force of gravity is
practically a constant equal to mg, directed
M
s M
E towards the centre of the earth. If we consider
a point at a height h from the surface of the
1
earth and another point vertically above it at a
height h from the surface, the work done in
2
lifting the particle of mass m from the first to
the second position is denoted by W
Fig. 8.8 (b) g at a depth d. In this case only the 12
W = Force × displacement
smaller sphere of radius (R –d) 12
E
contributes to g. = mg (h – h ) (8.20)
1
2
2018-19