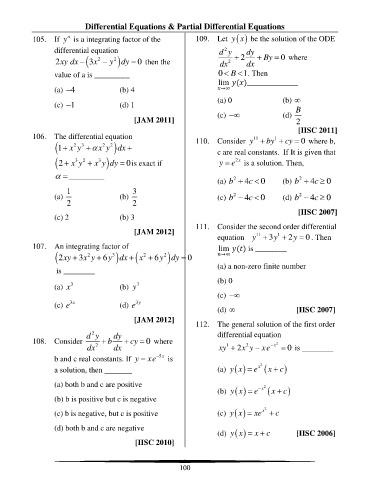
Page 102 - Engineering Mathematics Workbook_Final
P. 102
Differential Equations & Partial Differential Equations
y
a
105. If y is a integrating factor of the 109. Let ( ) x be the solution of the ODE
differential equation d y dy
2
2xy dx − (3x − y 2 ) dy = then the dx 2 + 2 dx + By = 0 where
2
0
value of a is _________ 0 B 1. Then
lim ( )_____________
−
(a) 4 (b) 4 →∞
−
(c) 1 (d) 1 (a) 0 (b)
B
(c) − (d)
[JAM 2011] 2
[IISC 2011]
106. The differential equation 110. Consider y + by + cy = 0 where b,
11
1
(1 x y+ 2 3 + x y 2 ) dx + c are real constants. If It is given that
2
2x
(2 x y + x 3 ) y dy = is exact if y = e is a solution. Then,
+
3
2
0
=_________ 2 2
(a) b + 4c 0 (b) b + 4c 0
1 3
(a) (b) (c) b − 2 4c 0 (d) b − 2 4c 0
2 2
[IISC 2007]
(c) 2 (b) 3
111. Consider the second order differential
[JAM 2012]
11
1
equation y + 3y + 2y = . Then
0
107. An integrating factor of lim ( ) is ________
(2xy + 3x y + 6y 3 ) dx + ( x + 6y 2 ) dy = 0 →∞
2
2
(a) a non-zero finite number
is ________
(b) 0
3
3
(a) x (b) y
(c) −
3y
3x
(c) e (d) e
(d) [IISC 2007]
[JAM 2012]
112. The general solution of the first order
2
d y dy differential equation
108. Consider + b + cy = 0 where 2
1
2
dx 2 dx xy + 2x y − xe − x = 0 is ________
b and c real constants. If y = xe − 5x is
)
+
a solution, then _______ (a) ( ) x = y e x 2 (x c
(a) both b and c are positive 2
)
+
(b) ( ) x = y e − x (x c
(b) b is positive but c is negative
(c) b is negative, but c is positive (c) ( ) x = y xe + x 2 c
(d) both b and c are negative
+
y
(d) ( ) x = x c [IISC 2006]
[IISC 2010]
100