Page 96 - Digital Electronics by harish
P. 96
output is 1111. The outputs of the counter during the application of each clock pulse are
shown in the waveforms.
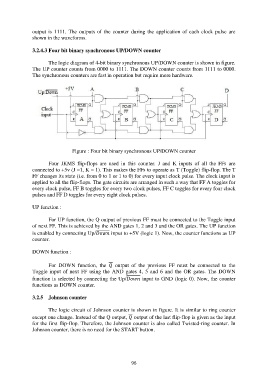
3.2.4.3 Four bit binary synchronous UP/DOWN counter
The logic diagram of 4-bit binary synchronous UP/DOWN counter is shown in figure.
The UP counter counts from 0000 to 1111. The DOWN counter counts from 1111 to 0000.
The synchronous counters are fast in operation but require more hardware.
Figure : Four bit binary synchronous UP/DOWN counter
Four JKMS flip-flops are used in this counter. J and K inputs of all the FFs are
connected to +5v (J =1, K = 1). This makes the FFs to operate as T (Toggle) flip-flop. The T
FF changes its state (i.e. from 0 to 1 or 1 to 0) for every input clock pulse. The clock input is
applied to all the flip-flops. The gate circuits are arranged in such a way that FF A toggles for
every clock pulse, FF B toggles for every two clock pulses, FF C toggles for every four clock
pulses and FF D toggles for every eight clock pulses.
UP function :
For UP function, the Q output of previous FF must be connected to the Toggle input
of next FF. This is achieved by the AND gates 1, 2 and 3 and the OR gates. The UP function
is enabled by connecting Up/ input to +5V (logic 1). Now, the counter functions as UP
counter.
DOWN function :
For DOWN function, the output of the previous FF must be connected to the
Toggle input of next FF using the AND gates 4, 5 and 6 and the OR gates. The DOWN
function is selected by connecting the Up/ input to GND (logic 0). Now, the counter
functions as DOWN counter.
3.2.5 Johnson counter
The logic circuit of Johnson counter is shown in figure. It is similar to ring counter
except one change. Instead of the Q output, output of the last flip-flop is given as the input
for the first flip-flop. Therefore, the Johnson counter is also called Twisted-ring counter. In
Johnson counter, there is no need for the START button.
96