Page 578 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 578
534 SecTioN iii Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—oPhthAlmology Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—oPhthAlmology
Vertigo Sensation of spinning while actually stationary. Subtype of “dizziness,” but distinct from
“lightheadedness.”
Peripheral vertigo More common. Inner ear etiology (eg, semicircular canal debris, vestibular nerve infection,
Ménière disease [triad: sensorineural hearing loss, vertigo, tinnitus; endolymphatic hydrops
endolymph within the inner ear], benign paroxysmal positional vertigo [BPPV]). Treatment:
antihistamines, anticholinergics, antiemetics (symptomatic relief); low-salt diet +/– diuretics
(Ménière disease); Epley maneuver (BPPV).
Central vertigo Brain stem or cerebellar lesion (eg, stroke affecting vestibular nuclei, demyelinating disease, or
posterior fossa tumor). Findings: directional or purely vertical nystagmus, skew deviation (vertical
misalignment of the eyes), diplopia, dysmetria. Focal neurologic findings.
` neurology—oPhthAlmology
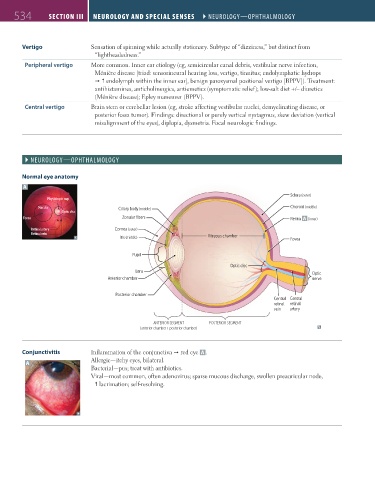
Normal eye anatomy
A
Sclera (outer)
Physiologic cup
Macula Ciliary body (middle) Choroid (middle)
Optic disc
A
Fovea Zonular fibers Retina (inner)
Retinal artery Cornea (outer)
Retinal vein
Iris (middle) Vitreous chamber Fovea
Pupil
Optic disc
Lens Optic
Anterior chamber nerve
Posterior chamber
Central Central
retinal retinal
vein artery
ANTERIOR SEGMENT POSTERIOR SEGMENT
(anterior chamber + posterior chamber)
Conjunctivitis Inflammation of the conjunctiva red eye A .
A Allergic—itchy eyes, bilateral.
Bacterial—pus; treat with antibiotics.
Viral—most common, often adenovirus; sparse mucous discharge, swollen preauricular node,
lacrimation; self-resolving.
FAS1_2019_12-Neurol.indd 534 11/8/19 7:39 AM