Page 579 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 579
Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—oPhthAlmology Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—oPhthAlmology SecTioN iii 535
Refractive errors Common cause of impaired vision, correctable with glasses.
Hyperopia Also called “farsightedness.” Eye too short for refractive power of cornea and lens light focused
behind retina. Correct with convex (converging) lenses.
Myopia Also called “nearsightedness.” Eye too long for refractive power of cornea and lens light focused
in front of retina. Correct with concave (diverging) lens.
Astigmatism Abnormal curvature of cornea different refractive power at different axes. Correct with
cylindrical lens.
Presbyopia Aging-related impaired accommodation (focusing on near objects), primarily due to lens elasticity,
changes in lens curvature, strength of the ciliary muscle. Patients often need “reading glasses”
(magnifiers).
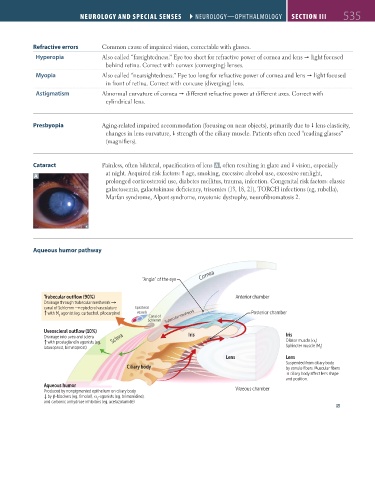
Cataract Painless, often bilateral, opacification of lens A , often resulting in glare and vision, especially
A at night. Acquired risk factors: age, smoking, excessive alcohol use, excessive sunlight,
prolonged corticosteroid use, diabetes mellitus, trauma, infection. Congenital risk factors: classic
galactosemia, galactokinase deficiency, trisomies (13, 18, 21), TORCH infections (eg, rubella),
Marfan syndrome, Alport syndrome, myotonic dystrophy, neurofibromatosis 2.
Aqueous humor pathway
Cornea
“Angle” of the eye
Trabecular outflow (90%) Anterior chamber
Drainage through trabecular meshwork ↓
canal of Schlemm episcleral vasculature Episcleral
↓
with M agonist (eg, carbachol, pilocarpine) vessels Posterior chamber
3 Canal of Trabecular meshwork
↓
Schlemm
Uveoscleral outflow (10%)
Drainage into uvea and sclera Sclera Iris Iris
with prostaglandin agonists (eg, Dilator muscle (α ) 1
latanoprost, bimatoprost) Sphincter muscle (M ) 3
↓
Lens Lens
Suspended from ciliary body
Ciliary body by zonule fibers. Muscular fibers
and position.
Aqueous humor
Produced by nonpigmented epithelium on ciliary body Vitreous chamber
↓ by β-blockers (eg, timolol), α -agonists (eg, brimonidine),
2
and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (eg, acetazolamide)
FAS1_2019_12-Neurol.indd 535 11/8/19 7:39 AM