Page 694 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 694
650 SectioN iii RepRoductive ` REPRODUCTIVE—PATHOlOgy RepRoductive ` REPRODUCTIVE—PATHOlOgy
Breast cancer Commonly postmenopausal. Often presents as a Risk factors in women: age; history of atypical
A palpable hard mass A most often in the upper hyperplasia; family history of breast cancer; race
outer quadrant. Invasive cancer can become (Caucasians at highest risk, African Americans at
fixed to pectoral muscles, deep fascia, Cooper risk for triple ⊝ breast cancer); BRCA1/BRCA2
ligaments, and overlying skin nipple mutations; estrogen exposure (eg, nulliparity);
retraction/skin dimpling. postmenopausal obesity (adipose tissue converts
Usually arises from terminal duct lobular unit. androstenedione to estrone); total number of
Amplification/overexpression of estrogen/ menstrual cycles; absence of breastfeeding; later
progesterone receptors or c-erbB2 (HER2, an age of first pregnancy; alcohol intake. In men:
EGF receptor) is common; triple negative BRCA2 mutation, Klinefelter syndrome.
(ER ⊝, PR ⊝, and HER2/neu ⊝) form more Axillary lymph node metastasis most important
aggressive. prognostic factor in early-stage disease.
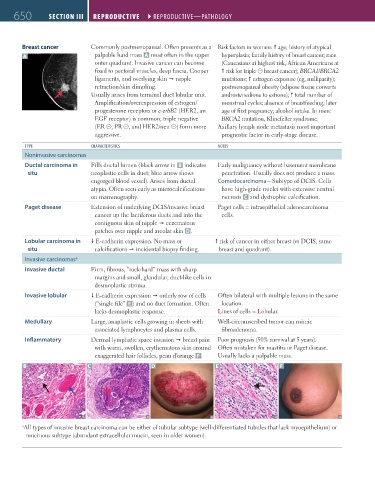
TyPE CHARACTERISTICS NOTES
Noninvasive carcinomas
Ductal carcinoma in Fills ductal lumen (black arrow in B indicates Early malignancy without basement membrane
situ neoplastic cells in duct; blue arrow shows penetration. Usually does not produce a mass.
engorged blood vessel). Arises from ductal Comedocarcinoma—Subtype of DCIS. Cells
atypia. Often seen early as microcalcifications have high-grade nuclei with extensive central
on mammography. necrosis C and dystrophic calcification.
Paget disease Extension of underlying DCIS/invasive breast Paget cells = intraepithelial adenocarcinoma
cancer up the lactiferous ducts and into the cells.
contiguous skin of nipple eczematous
patches over nipple and areolar skin D.
Lobular carcinoma in E-cadherin expression. No mass or risk of cancer in either breast (vs DCIS, same
situ calcifications incidental biopsy finding. breast and quadrant).
Invasive carcinomas a
Invasive ductal Firm, fibrous, “rock-hard” mass with sharp
margins and small, glandular, duct-like cells in
desmoplastic stroma.
Invasive lobular E-cadherin expression orderly row of cells Often bilateral with multiple lesions in the same
(“single file” E ) and no duct formation. Often location.
lacks desmoplastic response. Lines of cells = Lobular.
Medullary Large, anaplastic cells growing in sheets with Well-circumscribed tumor can mimic
associated lymphocytes and plasma cells. fibroadenoma.
Inflammatory Dermal lymphatic space invasion breast pain Poor prognosis (50% survival at 5 years).
with warm, swollen, erythematous skin around Often mistaken for mastitis or Paget disease.
exaggerated hair follicles, peau d’orange F . Usually lacks a palpable mass.
B C D E F
a All types of invasive breast carcinoma can be either of tubular subtype (well-differentiated tubules that lack myoepithelium) or
mucinous subtype (abundant extracellular mucin, seen in older women).
FAS1_2019_15-Repro.indd 650 11/7/19 5:52 PM