Page 21 - Spotlight A+ Form 4 & 5 Chemistry KSSM
P. 21
Form
4
Chapter 5 Chemical Bond Chemistry
Paper 2
Section A
SPM Clone [1 mark]
1. (a) (i) The electron arrangement of neon is 2.8. Why is this element very stable? C2
(ii) Name another element that has the same stability as neon. C1 [1 mark]
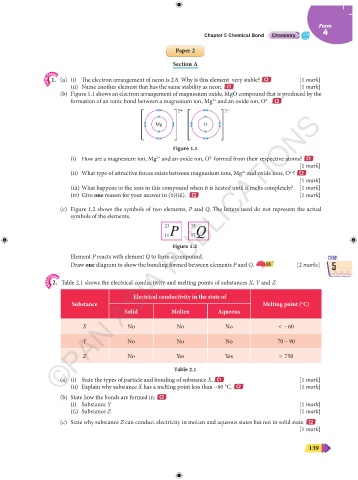
(b) Figure 1.1 shows an electron arrangement of magnesium oxide, MgO compound that is produced by the
2–
formation of an ionic bond between a magnesium ion, Mg and an oxide ion, O . C2
2+
2+ 2–
Mg O
Figure 1.1
(i) How are a magnesium ion, Mg and an oxide ion, O formed from their respective atoms? C1
2-
2+
[1 mark]
2-
(ii) What type of attractive forces exists between magnesium ions, Mg and oxide ions, O ? C2
2+
[1 mark]
(iii) What happens to the ions in this compound when it is heated until it melts completely? [1 mark]
(iv) Give one reason for your answer in (b)(iii). C2 [1 mark]
(c) Figure 1.2 shows the symbols of two elements, P and Q. The letters used do not represent the actual
symbols of the elements.
23 35
11P 17Q
Figure 1.2
Element P reacts with element Q to form a compound.
CHAP. ©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS CHAP.
5 Draw one diagram to show the bonding formed between elements P and Q. C6 [2 marks] 5
SPM Clone
2. Table 2.1 shows the electrical conductivity and melting points of substances X, Y and Z.
Electrical conductivity in the state of
Substance Melting point (°C)
Solid Molten Aqueous
X No No No < – 60
Y No No No 70 – 90
Z No Yes Yes > 750
Table 2.1
(a) (i) State the types of particle and bonding of substance X. C1 [1 mark]
(ii) Explain why substance X has a melting point less than – 60 °C. C2 [1 mark]
(b) State how the bonds are formed in: C2
(i) Substance Y [1 mark]
(ii) Substance Z [1 mark]
(c) State why substance Z can conduct electricity in molten and aqueous states but not in solid state. C2
[1 mark]
139