Page 32 - Spotlight A+ Form 4 & 5 Chemistry KSSM
P. 32
Form
5
Chapter 1 Redox Equilibrium Chemistry
CHAP. CHAP.
1 1.2 1
1. State the meaning of standard electrode potential, E . C1
0
2. What are the standard conditions for the measurement of standard electrode potential of a half-cell?
C1
0
3. Referring to the standard electrode potential, E given below, answer the following questions. C4
+
–
0
Ag (aq) + e Ag(s) E = +0.80 V
–
Sn (aq) + 2e Sn(s) E = –0.14 V
0
2+
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
(a) Determine the oxidising agent and substance to be oxidised.
(b) Write the oxidation half equation and reduction half equation.
(c) State two observations that can be obtained in the redox reaction.
(d) Construct an overall ionic equation to represent the reaction.
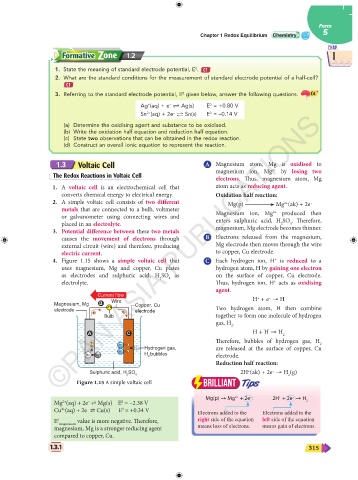
1.3 Voltaic Cell A Magnesium atom, Mg is oxidised to
2+
The Redox Reactions in Voltaic Cell magnesium ion, Mg by losing two
electrons. Thus, magnesium atom, Mg
1. A voltaic cell is an electrochemical cell that atom acts as reducing agent.
converts chemical energy to electrical energy. Oxidation half reaction:
2. A simple voltaic cell consists of two different Mg(p) Mg (ak) + 2e –
2+
metals that are connected to a bulb, voltmeter 2+
or galvanometer using connecting wires and Magnesium ion, Mg produced then
placed in an electrolyte. enters sulphuric acid, H SO . Therefore,
4
2
3. Potential difference between these two metals magnesium, Mg electrode becomes thinner.
causes the movement of electrons through B Electrons released from the magnesium,
external circuit (wire) and therefore, producing Mg electrode then moves through the wire
electric current. to copper, Cu electrode.
4. Figure 1.15 shows a simple voltaic cell that C Each hydrogen ion, H is reduced to a
+
uses magnesium, Mg and copper, Cu plates hydrogen atom, H by gaining one electron
as electrodes and sulphuric acid, H SO as on the surface of copper, Cu electrode.
2
4
+
electrolyte. Thus, hydrogen ion, H acts as oxidising
agent.
Current flow H + e → H
+
–
Wire
Magnesium, Mg B Copper, Cu
electrode electrode Two hydrogen atom, H then combine
e – e – together to form one molecule of hydrogen
Bulb
gas, H .
2
H + H → H
A C 2
Therefore, bubbles of hydrogen gas, H
e – 2
e – H + + e –
H 2 Hydrogen gas, are released at the surface of copper, Cu
H + + e –
Mg Mg 2+ H bubbles electrode.
2
Reduction half reaction:
+
–
Sulphuric acid, H SO 2H (ak) + 2e → H (g)
2 4 2
Figure 1.15 A simple voltaic cell
–
Mg(p) → Mg + 2e – 2H + 2e → H
+
2+
Mg (aq) + 2e ⇌ Mg(s) E = –2.38 V 2
2+
–
0
Cu (aq) + 2e ⇌ Cu(s) E = +0.34 V Electrons added to the Electrons added to the
–
2+
0
E 0 magnesium value is more negative. Therefore, right side of the equation left side of the equation
magnesium, Mg is a stronger reducing agent means loss of electrons. means gain of electrons.
compared to copper, Cu.
1.3.1 315