Page 37 - Spotlight A+ Form 4 & 5 Chemistry KSSM
P. 37
Form
5
Chapter 1 Redox Equilibrium Chemistry
CHAP. iron, Fe and are accepted by positive ions CHAP.
1 such as hydrogen ions, H or oxygen, O
2 1
+
Magnesium, Mg and iron, Fe form oxide coating and water, H O in the electrolyte.
2
which is porous , not tightly packed and weak.
This oxide coating is easily peeled off and cannot
protect the metals from corrosion.
Cars rust more rapidly in a country where salt is
used to melt the snow and ice on the road.
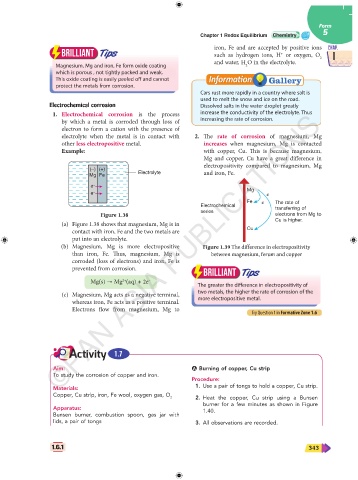
Electrochemical corrosion Dissolved salts in the water droplet greatly
1. Electrochemical corrosion is the process increase the conductivity of the electrolyte. Thus
Materials: ©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
by which a metal is corroded through loss of increasing the rate of corrosion.
electron to form a cation with the presence of
electrolyte when the metal is in contact with 2. The rate of corrosion of magnesium, Mg
other less electropositive metal. increases when magnesium, Mg is contacted
Example: with copper, Cu. This is because magnesium,
Mg and copper, Cu have a great difference in
electropositivity compared to magnesium, Mg
(–) (+) Electrolyte and iron, Fe.
Mg Fe
e –
Mg
e – e –
Fe e – The rate of
Electrochemical
transferring of
Figure 1.38 series electrons from Mg to
Cu is higher.
(a) Figure 1.38 shows that magnesium, Mg is in
contact with iron, Fe and the two metals are Cu
put into an electrolyte.
(b) Magnesium, Mg is more electropositive Figure 1.39 The difference in electropositivity
than iron, Fe. Thus, magnesium, Mg is between magnesium, ferum and copper
corroded (loss of electrons) and iron, Fe is
prevented from corrosion.
Mg(s) → Mg (aq) + 2e –
2+
The greater the difference in electropositivity of
(c) Magnesium, Mg acts as a negative terminal, two metals, the higher the rate of corrosion of the
more electropositive metal.
whereas iron, Fe acts as a positive terminal.
Electrons flow from magnesium, Mg to
Try Question 1 in Formative Zone 1.6
Activity 1.7
Aim: A Burning of copper, Cu strip
To study the corrosion of copper and iron.
Procedure:
1. Use a pair of tongs to hold a copper, Cu strip.
Copper, Cu strip, iron, Fe wool, oxygen gas, O
2 2. Heat the copper, Cu strip using a Bunsen
burner for a few minutes as shown in Figure
Apparatus: 1.40.
Bunsen burner, combustion spoon, gas jar with
lids, a pair of tongs 3. All observations are recorded.
1.6.1 343