Page 33 - Spotlight A+ Form 4 & 5 Chemistry KSSM
P. 33
Form
5 Chemistry Chapter 1 Redox Equilibrium
CHAP. 5. Redox reaction occurred in the simple chemical 7. The relative charge on the electrode depends CHAP.
1 cell can be represented by the following overall on the source of electrons and the direction of 1
ionic equation: flow of electrons.
(a) Since the electrons released by the
Oxidation half equation: Mg(s) → Mg (aq) + 2e – magnesium atom, Mg enters the
2+
Reduction half equation: 2H (aq) + 2e → H (g) magnesium, Mg electrode while the
–
+
2 electrons that reach the copper, Cu
Overall ionic equation: Mg(s) + 2H (aq) → Mg (aq) + H (g) electrode are given to the hydrogen ion,
+
2+
2
H , magnesium, Mg electrode relatively
+
6. The area where oxidation occurs is called anode contains more negative charge (electrons)
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
and the area where reduction occurs is called compare to copper, Cu electrode.
cathode. Thus, the magnesium, Mg electrode (b) Thus, magnesium, Mg electrode is the
acts as an anode while the copper, Cu electrode negative terminal of the cell and the
acts as a cathode in this simple chemical cell. copper, Cu electrode is the positive
terminal of the cell.
U seful Acronym (c) The potential difference between
magnesium, Mg and copper, Cu causes the
transfer of electrons through the external
circuit and an electric current is produced.
(d) Hydrogen gas, H on the copper, Cu surface
2
results in polarisation and prevents
further reduction of hydrogen ions,
+
Red cat An ox H . Hence, simple chemical cell can only
Reduction; cathode Oxidation; anode function for a short period of time.
8. This problem was solved by John Frederic
Daniell, a British chemist in 1836 who invented
Daniell cell.
1.1
Aim: Procedure:
To show the production of electricity through redox 1. A copper, Cu plate and iron, Fe nail are cleaned
reaction in a simple voltaic cell. with sandpaper.
3
-3
Problem statement: 2. 150 cm of 1.0 mol dm sulphuric acid, H SO is
2
4
How can a simple voltaic cell produce electricity poured into a beaker.
through redox reaction?
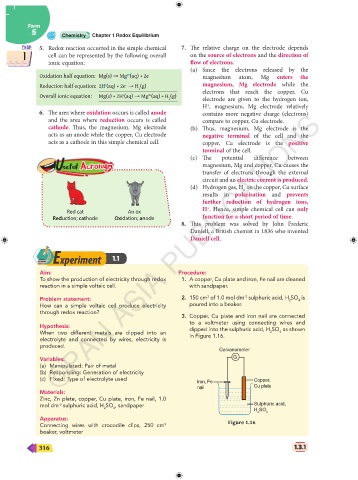
3. Copper, Cu plate and iron nail are connected
to a voltmeter using connecting wires and
Hypothesis: dipped into the sulphuric acid, H SO as shown
When two different metals are dipped into an in Figure 1.16. 2 4
electrolyte and connected by wires, electricity is
produced.
Galvanometer
G
Variables:
(a) Manipulated: Pair of metal
(b) Responding: Generation of electricity
(c) Fixed: Type of electrolyte used Iron, Fe Copper,
nail Cu plate
Materials:
Zinc, Zn plate, copper, Cu plate, iron, Fe nail, 1.0
-3
mol dm sulphuric acid, H SO , sandpaper Sulphuric acid,
2 4 H SO 4
2
Apparatus: Figure 1.16
3
Connecting wires with crocodile clips, 250 cm
beaker, voltmeter
316 1.3.1