Page 82 - Fisika Terapan for Engineers and Scientists
P. 82
282 CHAPTER 9 Gravitation
the following do we need: the period, the radius of the moon’s orbit, the mass of the
moon, the radius of the planet?
QUESTION 4: The radius of the orbit of Saturn around the Sun is about 10 times the
radius of the orbit of the Earth. Accordingly, what must be the approximate period of
its orbital motion?
(A) 1000 yr (B) 100 yr (C) 30 yr (D) 10 yr (E) 3 yr
Online 9.4 ELLIPTICAL ORBITS; KEPLER’S LAWS
12
Concept
Tutorial Although the orbits of the planets around the Sun are approximately circular, none of
these orbits are exactly circular. We will not attempt the general solution of the equa-
tion of motion for such noncircular orbits. A complete calculation shows that with
the inverse-square force of Eq. (9.1), the planetary orbits are ellipses.This is Kepler’s
First Law:
Kepler’s First Law The orbits of the planets are ellipses with the Sun at one focus.
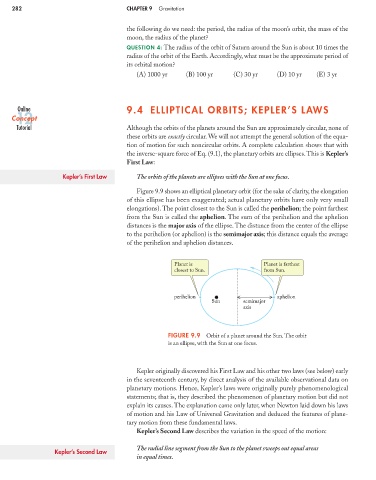
Figure 9.9 shows an elliptical planetary orbit (for the sake of clarity, the elongation
of this ellipse has been exaggerated; actual planetary orbits have only very small
elongations). The point closest to the Sun is called the perihelion; the point farthest
from the Sun is called the aphelion. The sum of the perihelion and the aphelion
distances is the major axis of the ellipse. The distance from the center of the ellipse
to the perihelion (or aphelion) is the semimajor axis; this distance equals the average
of the perihelion and aphelion distances.
Planet is Planet is farthest
closest to Sun. from Sun.
perihelion aphelion
Sun semimajor
axis
FIGURE 9.9 Orbit of a planet around the Sun. The orbit
is an ellipse, with the Sun at one focus.
Kepler originally discovered his First Law and his other two laws (see below) early
in the seventeenth century, by direct analysis of the available observational data on
planetary motions. Hence, Kepler’s laws were originally purely phenomenological
statements; that is, they described the phenomenon of planetary motion but did not
explain its causes. The explanation came only later, when Newton laid down his laws
of motion and his Law of Universal Gravitation and deduced the features of plane-
tary motion from these fundamental laws.
Kepler’s Second Law describes the variation in the speed of the motion:
The radial line segment from the Sun to the planet sweeps out equal areas
Kepler’s Second Law
in equal times.