Page 100 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 100
Plate 4-15 Integumentary System
CUTANEOUS LUPUS BAND TEST
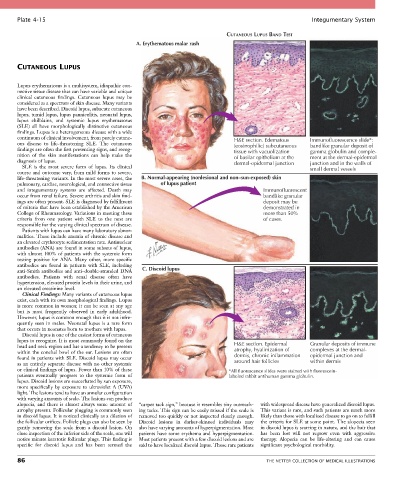
A. Erythematous malar rash
CUTANEOUS LUPUS
Lupus erythematosus is a multisystem, idiopathic con-
nective tissue disease that can have variable and unique
clinical cutaneous findings. Cutaneous lupus may be
considered as a spectrum of skin disease. Many variants
have been described. Discoid lupus, subacute cutaneous
lupus, tumid lupus, lupus panniculitis, neonatal lupus,
lupus chilblains, and systemic lupus erythematosus
(SLE) all have morphologically distinctive cutaneous
findings. Lupus is a heterogeneous disease with a wide
continuum of clinical involvement, from purely cutane- H&E section. Edematous Immunofluorescence slide*:
ous disease to life-threatening SLE. The cutaneous (eosinophilic) subcutaneous bandlike granular deposit of
findings are often the first presenting signs, and recog- tissue with vacuolization gamma globulin and comple-
nition of the skin manifestations can help make the of basilar epithelium at the ment at the dermal-epidermal
diagnosis of lupus. dermal-epidermal junction junction and in the walls of
SLE is the most severe form of lupus. Its clinical small dermal vessels
course and outcome vary, from mild forms to severe,
life-threatening variants. In the most severe cases, the B. Normal-appearing (nonlesional and non–sun-exposed) skin
pulmonary, cardiac, neurological, and connective tissue of lupus patient
and integumentary systems are affected. Death may Immunofluorescent
occur from renal failure. Severe arthritis and skin find- bandlike granular
ings are often present. SLE is diagnosed by fulfillment deposit may be
of criteria that have been established by the American demonstrated in
College of Rheumatology. Variations in meeting these more than 50%
criteria from one patient with SLE to the next are of cases.
responsible for the varying clinical spectrum of disease.
Patients with lupus can have many laboratory abnor-
malities. These include anemia of chronic disease and
an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Antinuclear
antibodies (ANA) are found in some subsets of lupus,
with almost 100% of patients with the systemic form
testing positive for ANA. Many other, more specific
antibodies are found in patients with SLE, including
anti-Smith antibodies and anti–double-stranded DNA C. Discoid lupus
antibodies. Patients with renal disease often have
hypertension, elevated protein levels in their urine, and
an elevated creatinine level.
Clinical Findings: Many variants of cutaneous lupus
exist, each with its own morphological findings. Lupus
is more common in women; it can be seen at any age
but is most frequently observed in early adulthood.
However, lupus is common enough that it is not infre-
quently seen in males. Neonatal lupus is a rare form
that occurs in neonates born to mothers with lupus.
Discoid lupus is one of the easiest forms of cutaneous
lupus to recognize. It is most commonly found on the
head and neck region and has a tendency to be present H&E section. Epidermal Granular deposits of immune
within the conchal bowl of the ear. Lesions are often atrophy, hyalinization of complexes at the dermal-
found in patients with SLE. Discoid lupus may occur dermis, chronic inflammation epidermal junction and
as an entirely separate disease with no other systemic around hair follicles within dermis
or clinical findings of lupus. Fewer than 10% of these *All fluorescence slides were stained with fluorescein-
patients eventually progress to the systemic form of labeled rabbit antihuman gamma globulin.
lupus. Discoid lesions are exacerbated by sun exposure,
more specifically by exposure to ultraviolet A (UVA)
light. The lesions tend to have an annular configuration
with varying amounts of scale. The lesions can produce
alopecia, and there is almost always some amount of “carpet tack sign,” because it resembles tiny outreach- with widespread disease have generalized discoid lupus.
atrophy present. Follicular plugging is commonly seen ing tacks. This sign can be easily missed if the scale is This variant is rare, and such patients are much more
in discoid lupus. It is noticed clinically as a dilation of removed too quickly or not inspected closely enough. likely than those with localized disease to go on to fulfill
the follicular orifices. Follicle plugs can also be seen by Discoid lesions in darker-skinned individuals may the criteria for SLE at some point. The alopecia seen
gently removing the scale from a discoid lesion. On also have varying amounts of hyperpigmentation. Most in discoid lupus is scarring in nature, and the hair that
close inspection of the inferior side of the scale, one will patients have some erythema and hyperpigmentation. has been lost will not regrow even with aggressive
notice minute keratotic follicular plugs. This finding is Most patients present with a few discoid lesions and are therapy. Alopecia can be life-altering and can cause
specific for discoid lupus and has been termed the said to have localized discoid lupus. Those rare patients significant psychological morbidity.
86 THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS