Page 101 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 101
Plate 4-16 Rashes
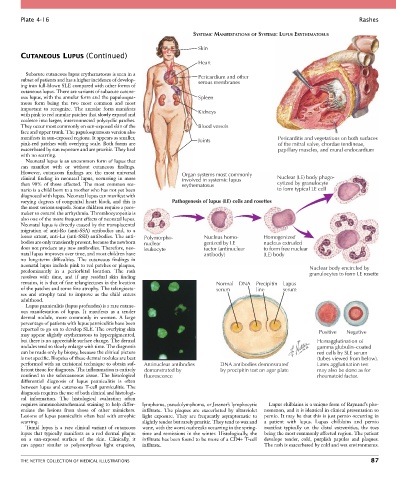
SYSTEMIC MANIFESTATIONS OF SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS
Skin
CUTANEOUS LUPUS (Continued)
Heart
Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus is seen in a
subset of patients and has a higher incidence of develop- Pericardium and other
serous membranes
ing into full-blown SLE compared with other forms of
cutaneous lupus. There are variants of subacute cutane-
ous lupus, with the annular form and the papulosqua- Spleen
mous form being the two most common and most
important to recognize. The annular form manifests
with pink to red annular patches that slowly expand and Kidneys
coalesce into larger, interconnected polycyclic patches.
They occur most commonly on sun-exposed skin of the Blood vessels
face and upper trunk. The papulosquamous version also
manifests in sun-exposed regions. It appears as smaller, Joints Pericarditis and vegetations on both surfaces
pink-red patches with overlying scale. Both forms are of the mitral valve, chordae tendineae,
exacerbated by sun exposure and are pruritic. They heal papillary muscles, and mural endocardium
with no scarring.
Neonatal lupus is an uncommon form of lupus that
can manifest with or without cutaneous findings.
However, cutaneous findings are the most universal Organ systems most commonly
clinical finding in neonatal lupus, occurring in more involved in systemic lupus Nuclear (LE) body phago-
than 90% of those affected. The most common sce- erythematosus cytized by granulocyte
nario is a child born to a mother who has not yet been to form typical LE cell
diagnosed with lupus. Neonatal lupus can manifest with
varying degrees of congenital heart block, and this is Pathogenesis of lupus (LE) cells and rosettes
the most serious sequela. Some children require a pace-
maker to control the arrhythmia. Thrombocytopenia is
also one of the more frequent effects of neonatal lupus.
Neonatal lupus is directly caused by the transplacental
migration of anti-Ro (anti-SSA) antibodies and, to a
lesser extent, anti-La (anti-SSB) antibodies. The anti- Polymorpho- Nucleus homo- Homogenized
bodies are only transiently present, because the newborn nuclear genized by LE nucleus extruded
does not produce any new antibodies. Therefore, neo- leukocyte factor (antinuclear to form free nuclear
natal lupus improves over time, and most children have antibody) (LE) body
no long-term difficulties. The cutaneous findings in
neonatal lupus include pink to red patches or plaques, Nuclear body encircled by
predominantly in a periorbital location. The rash granulocytes to form LE rosette
resolves with time, and if any residual skin finding
remains, it is that of fine telangiectases in the location Normal DNA Precipitin Lupus
of the patches and some fine atrophy. The telangiecta- serum line serum
ses and atrophy tend to improve as the child enters
adulthood.
Lupus panniculitis (lupus profundus) is a rare cutane-
ous manifestation of lupus. It manifests as a tender
dermal nodule, more commonly in women. A large
percentage of patients with lupus panniculitis have been
reported to go on to develop SLE. The overlying skin Positive Negative
may appear slightly erythematous to hyperpigmented,
but there is no appreciable surface change. The dermal Hemagglutination of
nodules tend to slowly enlarge with time. The diagnosis gamma globulin–coated
can be made only by biopsy, because the clinical picture red cells by SLE serum
is not specific. Biopsies of these dermal nodules are best (tubes viewed from below).
performed with an excisional technique to obtain suf- Antinuclear antibodies DNA antibodies demonstrated Latex agglutination test
ficient tissue for diagnosis. The inflammation is entirely demonstrated by by precipitin test on agar plate may also be done as for
confined to the subcutaneous tissue. The histological fluorescence rheumatoid factor.
differential diagnosis of lupus panniculitis is often
between lupus and cutaneous T-cell panniculitis. The
diagnosis requires the use of both clinical and histologi-
cal information. The histological evaluation often
requires immunohistochemical staining to help differ- lymphoma, pseudolymphoma, or Jessner’s lymphocytic Lupus chilblains is a unique form of Raynaud’s phe-
entiate the lesions from those of other mimickers. infiltrate. The plaques are exacerbated by ultraviolet nomenon, and it is identical in clinical presentation to
Lesions of lupus panniculitis often heal with atrophic light exposure. They are frequently asymptomatic to pernio. It may be that this is just pernio occurring in
scarring. slightly tender but rarely pruritic. They tend to wax and a patient with lupus. Lupus chilblains and pernio
Tumid lupus is a rare clinical variant of cutaneous wane, with the worst outbreaks occurring in the spring- manifest typically on the distal extremities, the toes
lupus that typically manifests as a red dermal plaque time and remissions in the winter. Histologically, the being the most commonly affected region. The patient
on a sun-exposed surface of the skin. Clinically, it infiltrate has been found to be more of a CD4+ T-cell develops tender, cold, purplish papules and plaques.
can appear similar to polymorphous light eruption, infiltrate. The rash is exacerbated by cold and wet environments.
THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS 87