Page 95 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 95
Plate 4-10 Rashes
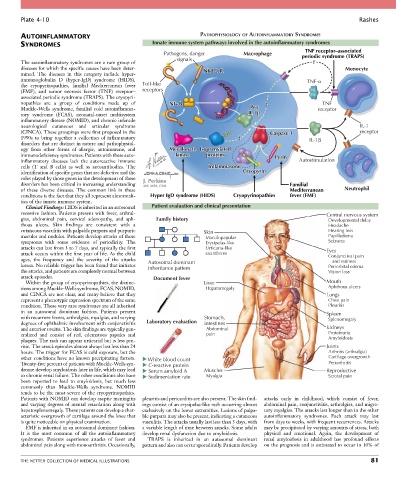
AUTOINFLAMMATORY PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF AUTOINFLAMMATORY SYNDROMES
SYNDROMES Innate immune system pathways involved in the autoinflammatory syndromes
TNF receptor–associated
Pathogens, danger Macrophage periodic syndrome (TRAPS)
signals
The autoinflammatory syndromes are a rare group of ?
diseases for which the specific causes have been deter- Nbd-LrR Monocyte
mined. The diseases in this category include hyper-
immunoglobulin D (hyper-IgD) syndrome (HIDS), TNF-
the cryopyrinopathies, familial Mediterranean fever Toll-like
(FMF), and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor– receptors
associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS). The cryopyri-
nopathies are a group of conditions made up of NF B ? ? TNF
Muckle-Wells syndrome, familial cold autoinflamma- Pro receptor
tory syndrome (FCAS), neonatal-onset multisystem IL-1
inflammatory disease (NOMID), and chronic infantile
neurological cutaneous and articular syndrome IL-1
(CINCA). These groupings were first proposed in the Caspase 1 receptor
1990s to bring together a collection of inflammatory ? ? IL-1
disorders that are distinct in nature and pathophysiol-
ogy from other forms of allergic, autoimmune, and Mevalonate Isoprenylated
immunodeficiency syndromes. Patients with these auto- kinase proteins Pyrin
inflammatory diseases lack the autoreactive immune Autostimulation
cells (T and B cells) as well as autoantibodies. The Inflammasome
identification of specific genes that are defective and the Cryopyrin
roles played by those genes in the development of these
disorders has been critical in increasing understanding Familial
of these diverse diseases. The common link in these Mediterranean Neutrophil
conditions is the fact that they all represent abnormali- Hyper IgD syndrome (HIDS) Cryopyrinopathies fever (FMF)
ties of the innate immune system.
Clinical Findings: HIDS is inherited in an autosomal Patient evaluation and clinical presentation
recessive fashion. Patients present with fever, arthral- Central nervous system
gias, abdominal pain, cervical adenopathy, and aph- Family history Developmental delay
thous ulcers. Skin findings are consistent with a Headache
cutaneous vasculitis with palpable purpura and purpuric Skin Hearing loss
macules and nodules. Patients develop attacks of these Maculopapular Papilledema
symptoms with some evidence of periodicity. The Erysipelas-like Seizures
attacks can last from 3 to 7 days, and typically the first Urticaria-like Eyes
attack occurs within the first year of life. As the child exanthems Conjunctival pain
ages, the frequency and the severity of the attacks Autosomal dominant and redness
lessen. No reliable trigger has been found that initiates inheritance pattern Periorbital edema
the attacks, and patients are completely normal between Vision loss
attack episodes. Document fever
Within the group of cryopyrinopathies, the distinc- Liver Mouth
tions among Muckle-Wells syndrome, FCAS, NOMID, Hepatomegaly Aphthous ulcers
and CINCA are not clear, and many believe that they Lungs
represent a phenotypic expression spectrum of the same Chest pain
condition. These very rare syndromes are all inherited Pleuritis
in an autosomal dominant fashion. Patients present Spleen
with recurrent fevers, arthralgias, myalgias, and varying Stomach, Splenomegaly
degrees of ophthalmic involvement with conjunctivitis Laboratory evaluation intestines
and anterior uveitis. The skin findings are typically gen- Abdominal Kidneys
eralized and consist of red, edematous papules and pain Proteinuria
plaques. The rash can appear urticarial but is less pru- Amyloidosis
ritic. The attack episodes almost always last less than 24 Joints
hours. The trigger for FCAS is cold exposure, but the Arthritis (arthralgia)
other conditions have no known precipitating factors. White blood count Cartilage overgrowth
Twenty-five percent of patients with Muckle-Wells syn- C-reactive protein Periarthritis
drome develop amyloidosis later in life, which may lead Serum amyloid A Muscles Reproductive
to chronic renal failure. The other conditions also have Sedimentation rate Myalgia Scrotal pain
been reported to lead to amyloidosis, but much less
commonly than Muckle-Wells syndrome. NOMID
tends to be the most severe of the cryopyrinopathies.
Patients with NOMID can develop aseptic meningitis pleuritis and pericarditis are also present. The skin find- attacks early in childhood, which consist of fever,
and varying degrees of mental retardation along with ings consist of an erysipelas-like rash occurring almost abdominal pain, conjunctivitis, arthralgias, and migra-
hepatosplenomegaly. These patients can develop a char- exclusively on the lower extremities. Lesions of palpa- tory myalgias. The attacks last longer than in the other
acteristic overgrowth of cartilage around the knee that ble purpura may also be present, indicating a cutaneous autoinflammatory syndromes. Each attack may last
is quite noticeable on physical examination. vasculitis. The attacks usually last less than 3 days, with from days to weeks, with frequent recurrences. Attacks
FMF is inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion. a variable length of time between attacks. Some adults may be precipitated by varying amounts of stress, both
It is the most common of all the autoinflammatory develop renal dysfunction due to amyloidosis. physical and emotional. Again, the development of
syndromes. Patients experience attacks of fever and TRAPS is inherited in an autosomal dominant renal amyloidosis in adulthood has profound effects
abdominal pain along with monoarthritis. Occasionally, pattern and also can occur sporadically. Patients develop on the prognosis and is estimated to occur in 10% of
THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS 81