Page 108 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 108
Plate 4-23 Integumentary System
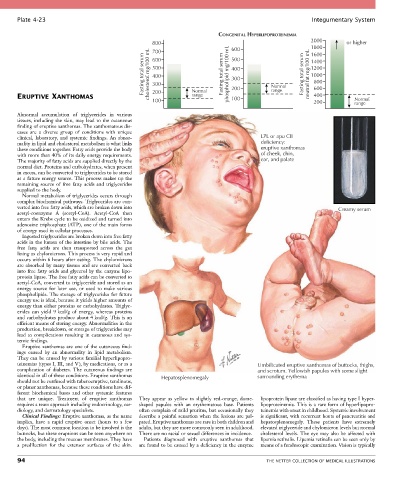
CONGENITAL HYPERLIPOPROTEINEMIA
800 600 2000 or higher
700
1600
Fasting total serum cholesterol mg/100 mL 600 Fasting total serum phospholipid mg/100 mL 500 Fasting total serum neutral fat mg/100 mL 1800
1400
1200
500
400
1000
400
300
800
300
range
range
400
ERUPTIVE XANTHOMAS 200 Normal 200 Normal 600 Normal
100
100
200
range
Abnormal accumulation of triglycerides in various
tissues, including the skin, may lead to the cutaneous
finding of eruptive xanthomas. The xanthomatous dis-
eases are a diverse group of conditions with unique
clinical, laboratory, and systemic findings. An abnor- LPL or apo CII
mality in lipid and cholesterol metabolism is what links deficiency:
these conditions together. Fatty acids provide the body eruptive xanthomas
with more than 40% of its daily energy requirements. of cheek, chin,
The majority of fatty acids are supplied directly by the ear, and palate
normal diet. Proteins and carbohydrates, when present
in excess, can be converted to triglycerides to be stored
as a future energy source. This process makes up the
remaining source of free fatty acids and triglycerides
supplied to the body.
Normal metabolism of triglycerides occurs through
complex biochemical pathways. Triglycerides are con-
verted into free fatty acids, which are broken down into Creamy serum
acetyl-coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA). Acetyl-CoA then
enters the Krebs cycle to be oxidized and turned into
adenosine triphosphate (ATP), one of the main forms
of energy used in cellular processes.
Ingested triglycerides are broken down into free fatty
acids in the lumen of the intestine by bile acids. The
free fatty acids are then transported across the gut
lining as chylomicrons. This process is very rapid and
occurs within 6 hours after eating. The chylomicrons
are absorbed by many tissues and are converted back
into free fatty acids and glycerol by the enzyme lipo-
protein lipase. The free fatty acids can be converted to
acetyl-CoA, converted to triglyceride and stored as an
energy source for later use, or used to make various
phospholipids. The storage of triglycerides for future
energy use is ideal, because it yields higher amounts of
energy than either proteins or carbohydrates. Triglyc-
erides can yield 9 kcal/g of energy, whereas proteins
and carbohydrates produce about 4 kcal/g. This is an
efficient means of storing energy. Abnormalities in the
production, breakdown, or storage of triglycerides may
lead to complications resulting in cutaneous and sys-
temic findings.
Eruptive xanthomas are one of the cutaneous find-
ings caused by an abnormality in lipid metabolism.
They can be caused by various familial hyperlipopro-
teinemias (types I, III, and V), by medications, or as a Umbilicated eruptive xanthomas of buttocks, thighs,
complication of diabetes. The cutaneous findings are and scrotum. Yellowish papules with some slight
identical in all of these conditions. Eruptive xanthomas Hepatosplenomegaly surrounding erythema
should not be confused with tuberoeruptive, tendinous,
or planar xanthomas, because these conditions have dif-
ferent biochemical bases and other systemic features
that are unique. Treatment of eruptive xanthomas They appear as yellow to slightly red-orange, dome- lipoprotein lipase are classified as having type I hyper-
requires a team approach including endocrinology, car- shaped papules with an erythematous base. Patients lipoproteinemia. This is a rare form of hyperlipopro-
diology, and dermatology specialists. often complain of mild pruritus, but occasionally they teinemia with onset in childhood. Systemic involvement
Clinical Findings: Eruptive xanthomas, as the name describe a painful sensation when the lesions are pal- is significant, with recurrent bouts of pancreatitis and
implies, have a rapid eruptive onset (hours to a few pated. Eruptive xanthomas are rare in both children and hepatosplenomegaly. These patients have extremely
days). The most common location to be involved is the adults, but they are more commonly seen in adulthood. elevated triglyceride and chylomicron levels but normal
buttocks, but these eruptions can be seen anywhere on There are no racial or sexual differences in incidence. cholesterol levels. The eye may also be affected with
the body, including the mucous membranes. They have Patients diagnosed with eruptive xanthomas that lipemia retinalis. Lipemia retinalis can be seen only by
a predilection for the extensor surfaces of the skin. are found to be caused by a deficiency in the enzyme means of a funduscopic examination. Vision is typically
94 THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS