Page 109 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 109
Plate 4-24 Rashes
ACQUIRED HYPERLIPOPROTEINEMIA
ERUPTIVE XANTHOMAS
(Continued)
normal, and the patient is unaware of any eye abnor-
malities. The blood vessels within the eye have a creamy
white color because of the excess lipid in the blood-
stream. The arteries and veins are equally affected, and
the only way to differentiate the two is by comparing
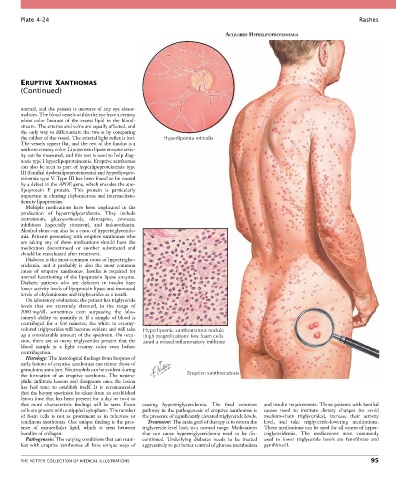
the caliber of the vessel. The arterial light reflex is lost. Hyperlipemia retinalis
The vessels appear flat, and the rest of the fundus is a
uniform creamy color. Lipoprotein lipase enzyme activ-
ity can be measured, and this test is used to help diag-
nosis type I hyperlipoproteinemia. Eruptive xanthomas
can also be seen as part of hyperlipoproteinemia type
III (familial dysbetalipoproteinemia) and hyperlipopro-
teinemia type V. Type III has been found to be caused
by a defect in the APOE gene, which encodes the apo-
lipoprotein E protein. This protein is particularly
important in clearing chylomicrons and intermediate-
density lipoproteins.
Multiple medications have been implicated in the
production of hypertriglyceridemia. They include
isotretinoin, glucocorticoids, olanzapine, protease
inhibitors (especially ritonavir), and indomethacin.
Alcohol abuse can also be a cause of hypertriglyceride-
mia. Patients presenting with eruptive xanthomas who
are taking any of these medications should have the
medication discontinued or another substituted and
should be reevaluated after treatment.
Diabetes is the most common cause of hypertriglyc-
eridemia, and it probably is also the most common
cause of eruptive xanthomas. Insulin is required for
normal functioning of the lipoprotein lipase enzyme.
Diabetic patients who are deficient in insulin have
lower activity levels of lipoprotein lipase and increased
levels of chylomicrons and triglycerides as a result.
On laboratory evaluation, the patient has triglyceride
levels that are extremely elevated, in the range of
2000 mg/dL sometimes even surpassing the labo-
ratory’s ability to quantify it. If a sample of blood is
centrifuged for a few minutes, the white to creamy-
colored triglycerides will become evident and will take Hyperlipemic xanthomatous nodule
up a considerable amount of the specimen. On occa- (high magnification): few foam cells
sion, there are so many triglycerides present that the amid a mixed inflammatory infiltrate
blood sample is a light creamy color even before
centrifugation.
Histology: The histological findings from biopsies of
early lesions of eruptive xanthomas can mimic those of
granuloma annulare. Neutrophils can be evident during
the formation of an eruptive xanthoma. The neutro- Eruptive xanthomatosis
philic infiltrate lessens and disappears once the lesion
has had time to establish itself. It is recommended
that the biopsy specimen be taken from an established
lesion (one that has been present for a day or two) so
that more characteristic findings will be seen. Foam causing hypertriglyceridemia. The final common and insulin requirements. Those patients with familial
cells are present with a stippled cytoplasm. The number pathway in the pathogenesis of eruptive xanthomas is causes need to institute dietary changes (to avoid
of foam cells is not as prominent as in tuberous or the presence of significantly elevated triglyceride levels. medium-chain triglycerides), increase their activity
tendinous xanthomas. One unique finding is the pres- Treatment: The main goal of therapy is to return the level, and take triglyceride-lowering medications.
ence of extracellular lipid, which is seen between triglyceride level back to a normal range. Medications These medications can be used for all causes of hyper-
bundles of collagen. that can cause hypertriglyceridemia need to be dis- triglyceridemia. The medications most commonly
Pathogenesis: The varying conditions that can mani- continued. Underlying diabetes needs to be treated used to lower triglyceride levels are fenofibrate and
fest with eruptive xanthomas all have unique ways of aggressively to get better control of glucose metabolism gemfibrozil.
THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS 95