Page 115 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 115
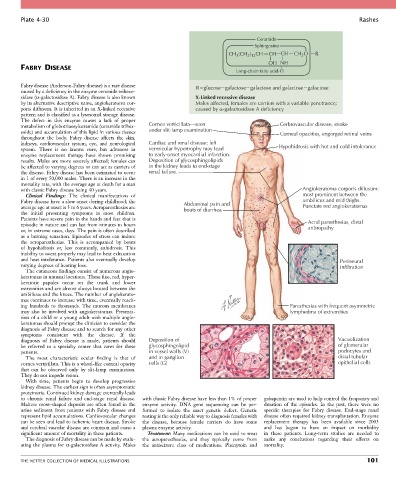
Plate 4-30 Rashes
Ceramide
Sphingosine
CH (CH ) CH CH CH CH 2 O R
2 12
3
OH NH
FABRY DISEASE
Long-chain fatty acid-O
Fabry disease (Anderson-Fabry disease) is a rare disease R glucose galactose galactose and galactose galactose
caused by a deficiency in the enzyme ceramide trihexo-
sidase (α-galactosidase A). Fabry disease is also known X-Linked recessive disease
by its alternative descriptive name, angiokeratoma cor- Males affected, females are carriers with a variable penetrance;
poris diffusum. It is inherited in an X-linked recessive caused by -galactosidase A deficiency
pattern and is classified as a lysosomal storage disease.
The defect in this enzyme causes a lack of proper
metabolism of globotriaosylceramide (ceramide trihex- Cornea verticillata—seen Cerbrovascular disease, stroke
oside) and accumulation of this lipid in various tissues under slit-lamp examination Corneal opacities, engorged retinal veins
throughout the body. Fabry disease affects the skin,
kidneys, cardiovascular system, eye, and neurological Cardiac and renal disease: left Hypohidrosis with hot and cold intolerance
system. There is no known cure, but advances in ventricular hypertrophy may lead
enzyme replacement therapy have shown promising to early-onset myocardial infarction.
results. Males are more severely affected; females can Deposition of glycosphingolipids
be affected to varying degrees or can act as carriers of in the kidney leads to end-stage
the disease. Fabry disease has been estimated to occur renal failure.
in 1 of every 50,000 males. There is an increase in the
mortality rate, with the average age at death for a man
with classic Fabry disease being 40 years. Angiokeratoma corporis diffusum:
Clinical Findings: The clinical manifestations of most prominent between the
Fabry disease have a slow onset during childhood; the Abdominal pain and umbilicus and mid thighs.
average age at onset is 5 to 6 years. Acroparesthesias are bouts of diarrhea Punctate red angiokeratomas
the initial presenting symptoms in most children.
Patients have severe pain in the hands and feet that is
episodic in nature and can last from minutes to hours Acral paresthesias, distal
or, in extreme cases, days. The pain is often described arthropathy
as a burning sensation. Episodes of stress can induce
the acroparesthesias. This is accompanied by bouts
of hypohidrosis or, less commonly, anhidrosis. This
inability to sweat properly may lead to heat exhaustion
and heat intolerance. Patients also eventually develop Perineural
varying degrees of hearing loss. infiltration
The cutaneous findings consist of numerous angio-
keratomas in unusual locations. These fine, red, hyper-
keratotic papules occur on the trunk and lower
extremities and are almost always located between the
umbilicus and the knees. The number of angiokerato-
mas continues to increase with time, eventually reach-
ing hundreds to thousands. The mucous membranes Paresthesias with frequent asymmetric
may also be involved with angiokeratomas. Presenta- lymphedma of extremities
tion of a child or a young adult with multiple angio-
keratomas should prompt the clinician to consider the
diagnosis of Fabry disease and to search for any other
symptoms consistent with the disease. If the
diagnosis of Fabry disease is made, patients should Deposition of Vacuolization
be referred to a specialty center that cares for these glycosphingolipid G of glomerular
patients. in vessel walls (V) podocytes and
The most characteristic ocular finding is that of and in ganglion V distal tubular
cornea verticillata. This is a whorl-like corneal opacity cells (G) epithelial cells
that can be observed only by slit-lamp examination.
They do not impede vision.
With time, patients begin to develop progressive
kidney disease. The earliest sign is often asymptomatic
proteinuria. Continued kidney damage eventually leads
to chronic renal failure and end-stage renal disease. with classic Fabry disease have less than 1% of proper gabapentin are used to help control the frequency and
Maltese cross–shaped deposits are often found in the enzyme activity. DNA gene sequencing can be per- duration of the episodes. In the past, there were no
urine sediment from patients with Fabry disease and formed to isolate the exact genetic defect. Genetic specific therapies for Fabry disease. End-stage renal
represent lipid accumulations. Cardiovascular changes testing is the only reliable way to diagnosis females with disease often required kidney transplantation. Enzyme
can be seen and lead to ischemic heart disease. Stroke the disease, because female carriers do have some replacement therapy has been available since 2003
and cerebral vascular disease are common and cause a plasma enzyme activity. and has begun to have an impact on morbidity
significant amount of mortality in these patients. Treatment: Many medications can be used to treat in these patients. Long-term studies are needed to
The diagnosis of Fabry disease can be made by evalu- the acroparesthesias, and they typically come from make any conclusions regarding their effects on
ating the plasma for α-galactosidase A activity. Males the antiseizure class of medications. Phenytoin and mortality.
THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS 101