Page 118 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 118
Plate 4-33 Integumentary System
TOPHACEOUS GOUT
GOUT (Continued)
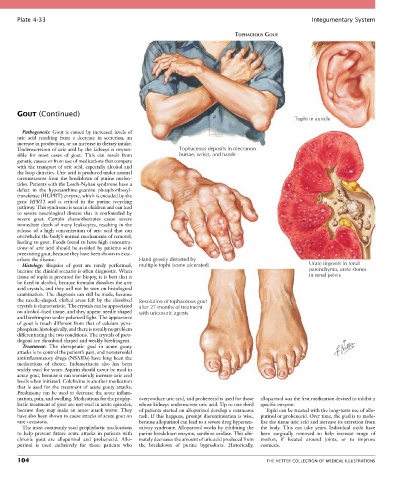
Tophi in auricle
Pathogenesis: Gout is caused by increased levels of
uric acid resulting from a decrease in secretion, an
increase in production, or an increase in dietary intake.
Underexcretion of uric acid by the kidneys is respon- Tophaceous deposits in olecranon
sible for most cases of gout. This can result from bursae, wrists, and hands
genetic causes or from use of medications that compete
with the transport of uric acid, especially alcohol and
the loop diuretics. Uric acid is produced under normal
circumstances from the breakdown of purine nucleo-
tides. Patients with the Lesch-Nyhan syndrome have a
defect in the hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl-
transferase (HGPRT) enzyme, which is encoded by the
gene HPRT1 and is critical in the purine recycling
pathway. This syndrome is seen in children and can lead
to severe neurological disease that is confounded by
severe gout. Certain chemotherapies cause severe
immediate death of many leukocytes, resulting in the
release of a high concentration of uric acid that can
overwhelm the body’s normal mechanisms of removal,
leading to gout. Foods found to have high concentra-
tions of uric acid should be avoided by patients with
preexisting gout, because they have been shown to exac-
erbate the disease. Hand grossly distorted by
Histology: Biopsies of gout are rarely performed, multiple tophi (some ulcerated) Urate deposits in renal
because the clinical scenario is often diagnostic. When parenchyma, urate stones
tissue of tophi is procured for biopsy, it is best that it in renal pelvis
be fixed in alcohol, because formalin dissolves the uric
acid crystals, and they will not be seen on histological
examination. The diagnosis can still be made, because
the needle-shaped, clefted areas left by the dissolved Resolution of tophaceous gout
crystals is characteristic. The crystals can be appreciated after 27 months of treatment
on alcohol-fixed tissue, and they appear needle shaped with uricosuric agents
and birefringent under polarized light. The appearance
of gout is much different from that of calcium pyro-
phosphate histologically, and there is usually no problem
differentiating the two conditions. The crystals of pseu-
dogout are rhomboid shaped and weakly birefringent.
Treatment: The therapeutic goal in acute gouty
attacks is to control the patient’s pain, and nonsteroidal
antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) have long been the
medications of choice. Indomethacin also has been
widely used for years. Aspirin should never be used in
acute gout, because it can transiently increase uric acid
levels when initiated. Colchicine is another medication
that is used for the treatment of acute gouty attacks.
Prednisone can be used to decrease the acute inflam-
mation, pain, and swelling. Medications for the prophy- overproduce uric acid, and probenecid is used for those allopurinol was the first medication devised to inhibit a
lactic treatment of gout are not used in acute episodes, whose kidneys underexcrete uric acid. Up to one third specific enzyme.
because they may make an acute attack worse. They of patients started on allopurinol develop a cutaneous Tophi can be treated with the long-term use of allo-
have also been shown to cause attacks of acute gout on rash. If this happens, prompt discontinuation is wise, purinol or probenecid. Over time, the goal is to mobi-
rare occasions. because allopurinol can lead to a severe drug hypersen- lize the tissue uric acid and increase its excretion from
The most commonly used prophylactic medications sitivity syndrome. Allopurinol works by inhibiting the the body. This can take years. Individual tophi have
to help prevent future acute attacks in patients with purine breakdown enzyme, xanthine oxidase. This ulti- been surgically removed to help increase range of
chronic gout are allopurinol and probenecid. Allo- mately decreases the amount of uric acid produced from motion, if located around joints, or to improve
purinol is used exclusively for those patients who the breakdown of purine byproducts. Historically, cosmesis.
104 THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS