Page 117 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 117
Plate 4-32 Rashes
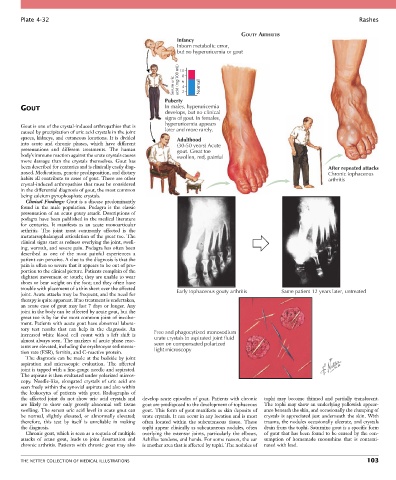
GOUTY ARTHRITIS
Infancy
Inborn metabolic error,
but no hyperuricemia or gout
8 –
Serum uric acid (mg/100 mL) 10 – Normal
6 –
4 –
2 –
Puberty
GOUT In males, hyperuricemia
develops, but no clinical
signs of gout. In females,
Gout is one of the crystal-induced arthropathies that is hyperuricemia appears
caused by precipitation of uric acid crystals in the joint later and more rarely.
spaces, kidneys, and cutaneous locations. It is divided Adulthood
into acute and chronic phases, which have different (30-50 years) Acute
presentations and different treatments. The human gout. Great toe
body’s immune reaction against the urate crystals causes swollen, red, painful
more damage than the crystals themselves. Gout has
been described for centuries and is clinically easily diag- After repeated attacks
nosed. Medications, genetic predisposition, and dietary Chronic tophaceous
habits all contribute to cases of gout. There are other arthritis
crystal-induced arthropathies that must be considered
in the differential diagnosis of gout, the most common
being calcium pyrophosphate crystals.
Clinical Findings: Gout is a disease predominantly
found in the male population. Podagra is the classic
presentation of an acute gouty attack. Descriptions of
podagra have been published in the medical literature
for centuries. It manifests as an acute monoarticular
arthritis. The joint most commonly affected is the
metatarsophalangeal articulation of the great toe. The
clinical signs start as redness overlying the joint, swell-
ing, warmth, and severe pain. Podagra has often been
described as one of the most painful experiences a
patient can perceive. A clue to the diagnosis is that the
pain is often so severe that it appears to be out of pro-
portion to the clinical picture. Patients complain of the
slightest movement or touch; they are unable to wear
shoes or bear weight on the foot; and they often have
trouble with placement of a thin sheet over the affected Early tophaceous gouty arthritis Same patient 12 years later, untreated
joint. Acute attacks may be frequent, and the need for
therapy is quite apparent. If no treatment is undertaken,
an acute case of gout may last 7 days or longer. Any
joint in the body can be affected by acute gout, but the
great toe is by far the most common joint of involve-
ment. Patients with acute gout have abnormal labora-
tory test results that can help in the diagnosis. An
increased white blood cell count with a left shift is Free and phagocytized monosodium
almost always seen. The markers of acute phase reac- urate crystals in aspirated joint fluid
tants are elevated, including the erythrocyte sedimenta- seen on compensated polarized
tion rate (ESR), ferritin, and C-reactive protein. light microscopy
The diagnosis can be made at the bedside by joint
aspiration and microscopic evaluation. The affected
joint is tapped with a fine-gauge needle and aspirated.
The aspirate is then evaluated under polarized micros-
copy. Needle-like, elongated crystals of uric acid are
seen freely within the synovial aspirate and also within
the leukocytes of patients with gout. Radiographs of
the affected joint do not show uric acid crystals and develop acute episodes of gout. Patients with chronic tophi may become thinned and partially translucent.
are likely to show only grossly abnormal soft tissue gout are predisposed to the development of tophaceous The tophi may show an underlying yellowish appear-
swelling. The serum uric acid level in acute gout can gout. This form of gout manifests as skin deposits of ance beneath the skin, and occasionally the clumping of
be normal, slightly elevated, or abnormally elevated; urate crystals. It can occur in any location and is most crystals is appreciated just underneath the skin. With
therefore, this test by itself is unreliable in making often located within the subcutaneous tissue. These trauma, the nodules occasionally ulcerate, and crystals
the diagnosis. tophi appear clinically as subcutaneous nodules, often drain from the tophi. Saturnine gout is a specific form
Chronic gout, which is seen as a sequela of multiple overlying the extensor joints, particularly the elbows, of gout that has been found to be caused by the con-
attacks of acute gout, leads to joint destruction and Achilles tendons, and hands. For some reason, the ear sumption of homemade moonshine that is contami-
chronic arthritis. Patients with chronic gout may also is another area that is affected by tophi. The nodules of nated with lead.
THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS 103