Page 151 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 151
Plate 4-66 Rashes
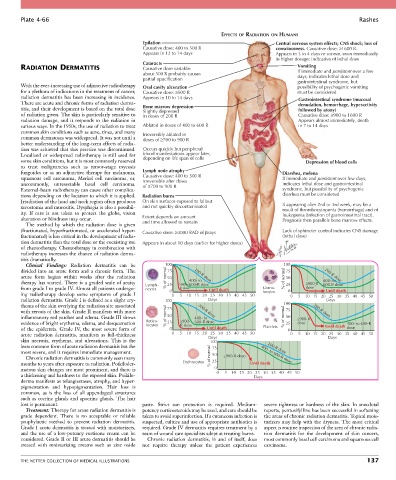
EFFECTS OF RADIATION ON HUMANS
Epilation Central nervous system effects; CNS shock; loss of
Causative dose: 400 to 500 R consciousness. Causative dose: ≥1600 R.
Appears in 12 to 14 days Appears in 3 to 4 days or sooner, even immediately
in higher dosage: indicative of lethal dose
Cataracts
RADIATION DERMATITIS Causative dose variable: Vomiting
about 500 R probably causes If immediate and persistent over a few
partial opacification days, indicates lethal dose and
gastrointestinal syndrome, but
With the ever-increasing use of adjunctive radiotherapy Oral cavity ulceration possibility of psychogenic vomiting
for a plethora of indications in the treatment of cancer, Causative dose: ≥500 R must be considered
radiation dermatitis has been increasing in incidence. Appears in 10 to 14 days Gastrointestinal syndrome (mucosal
There are acute and chronic forms of radiation derma- denudation, hemorrhage, hyperactivity
titis, and their development is based on the total dose Bone marrow depression followed by atony)
Slightly depressed
of radiation given. The skin is particularly sensitive to in doses of 200 R Causative dose: ≥900 to 1600 R
radiation damage, and it responds to the radiation in Appears almost immediately, death
various ways. In the 1950s, the use of radiation to treat Ablated in doses of 400 to 600 R in 7 to 14 days
common skin conditions such as acne, tinea, and many Irreversibly ablated in
common dermatoses was widespread. It was not until a doses of ≥700 to 900 R
better understanding of the long-term effects of radia-
tion was achieved that this practice was discontinued. Occurs quickly but peripheral
Localized or widespread radiotherapy is still used for blood manifestations appear later,
some skin conditions, but it is most commonly reserved depending on life span of cells Depression of blood cells
to treat malignancies such as tumor-stage mycosis
fungoides or as an adjunctive therapy for melanoma, Lymph node atrophy Diarrhea, melena
squamous cell carcinoma, Merkel cell carcinoma, or, Causative dose: 400 to 500 R If immediate and persistent over few days,
uncommonly, unresectable basal cell carcinoma. Irreversible after doses indicates lethal dose and gastrointestinal
of ≥700 to 900 R
External-beam radiotherapy can cause other complica- syndrome, but possibility of psychogenic
tions depending on the location to which it is applied. Radiation burns diarrhea must be considered
Irradiation of the head and neck region often produces On skin surfaces exposed to fallout
xerostomia and mucositis. Dysphagia is also a possibil- and not quickly decontaminated If appearing after 2nd or 3rd week, may be a
result of thrombocytopenia (hemorrhage) and of
ity. If care is not taken to protect the globe, vision leukopenia (infection of gastrointestinal tract).
alteration or blindness may occur. Extent depends on amount Prognosis then parallels bone marrow effects.
The method by which the radiation dose is given and time allowed to remain
(fractionated, hyperfractionated, or accelerated hyper- Causative dose: ≥4000 RAD of rays Lack of sphincter control indicates CNS damage
fractionated) is less critical in the development of radia- (lethal dose)
tion dermatitis than the total dose or the coexisting use Appears in about 10 days (earlier for higher doses)
of chemotherapy. Chemotherapy in combination with
radiotherapy increases the chance of radiation derma-
titis dramatically.
Clinical Findings: Radiation dermatitis can be 100 100
divided into an acute form and a chronic form. The 75 75
acute form begins within weeks after the radiation % of normal 50 200-R dose % of normal 50 200-R dose
therapy has started. There is a graded scale of acuity Lymph- 25 ≥900- 400- to 25 ≥900-R 400- to
600-R dose
600-R dose
from grade I to grade IV. Almost all patients undergo- ocytes 0 R dose Until death Granu- 0 dose Until death
ing radiotherapy develop some symptoms of grade I 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 locytes 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50
radiation dermatitis. Grade I is defined as a slight ery- 100 Days Days
thema of the skin overlying the radiation site associated 75 100
with xerosis of the skin. Grade II manifests with more 200-R dose 75 200-R dose
inflammatory red patches and edema. Grade III shows % of normal 50 400- to % of normal 50 ≥900-R
evidence of bright erythema, edema, and desquamation Reticu- 25 ≥900- 600-R dose 25 dose 400- to 600-R
locytes
R dose
of the epidermis. Grade IV, the most severe form of 0 Until death Platelets 0 Until death dose
acute radiation dermatitis, manifests as full-thickness 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50
Days
Days
skin necrosis, erythema, and ulcerations. This is the 100
least common form of acute radiation dermatitis but the 75 200-R dose
most severe, and it requires immediate management. 50 400- to 600-R dose
Chronic radiation dermatitis is commonly seen many % of normal ≥900-R dose
months to years after exposure to radiation. Poikiloder- Erythrocytes 25 Until death
matous skin changes are most prominent, and there is 0
a thickening and hardness to the exposed skin. Poikilo- 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50
Days
derma manifests as telangiectases, atrophy, and hyper-
pigmentation and hypopigmentation. Hair loss is
common, as is the loss of all appendageal structures
such as eccrine glands and apocrine glands. The hair
loss is permanent. paste. Strict sun protection is required. Medium- severe tightness or hardness of the skin. In anecdotal
Treatment: Therapy for acute radiation dermatitis is potency corticosteroids may be used, and care should be reports, pentoxifylline has been successful in softening
grade dependent. There is no acceptable or reliable taken to avoid superinfection. If a cutaneous infection is the areas of chronic radiation dermatitis. Topical mois-
prophylactic method to prevent radiation dermatitis. suspected, culture and use of appropriate antibiotics is turizers may help with the dryness. The most critical
Grade I acute dermatitis is treated with moisturizers, required. Grade IV dermatitis requires treatment by a aspect is routine inspection of the area of chronic radia-
and the use of a low-potency cortisone cream can be team of wound care specialists adept at treating burns. tion dermatitis for the development of skin cancers,
considered. Grade II or III acute dermatitis should be Chronic radiation dermatitis, in and of itself, does most commonly basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell
treated with moisturizing creams such as zinc oxide not require therapy unless the patient experiences carcinoma.
THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS 137