Page 156 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 156
Plate 4-71 Integumentary System
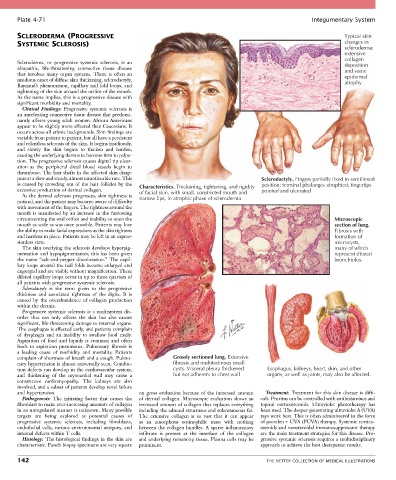
SCLERODERMA (PROGRESSIVE Typical skin
SYSTEMIC SCLEROSIS) changes in
scleroderma:
extensive
collagen
Scleroderma, or progressive systemic sclerosis, is an deposition
idiopathic, life-threatening connective tissue disease and some
that involves many organ systems. There is often an epidermal
insidious onset of diffuse skin thickening, sclerodactyly, atrophy
Raynaud’s phenomenon, capillary nail fold loops, and
tightening of the skin around the orifice of the mouth.
As the name implies, this is a progressive disease with
significant morbidity and mortality.
Clinical Findings: Progressive systemic sclerosis is
an unrelenting connective tissue disease that predomi-
nantly affects young adult women. African Americans
appear to be slightly more affected than Caucasians. It
occurs across all ethnic backgrounds. Skin findings are
variable from patient to patient, but all have a persistent
and relentless sclerosis of the skin. It begins insidiously,
and slowly the skin begins to thicken and harden,
causing the underlying dermis to become firm to palpa-
tion. The progressive sclerosis causes digital tip ulcer-
ation as the peripheral distal blood vessels begin to
thrombose. The hair shafts in the affected skin disap-
pear at a slow and steady, almost unnoticeable rate. This Sclerodactyly. Fingers partially fixed in semiflexed
is caused by crowding out of the hair follicles by the Characteristics. Thickening, tightening, and rigidity position; terminal phalanges atrophied; fingertips
excessive production of dermal collagen. of facial skin, with small, constricted mouth and pointed and ulcerated
As the dermal sclerosis progresses, skin tightness is
noticed, and the patient may become aware of difficulty narrow lips, in atrophic phase of scleroderma
with movement of the fingers. The tightness around the
mouth is manifested by an increase in the furrowing
circumventing the oral orifice and inability to open the Microscopic
mouth as wide as was once possible. Patients may lose section of lung.
the ability to make facial expressions as the skin tightens Fibrosis with
and hardens in place. Patients may be left in an expres- formation of
sionless state. microcysts,
The skin overlying the sclerosis develops hyperpig- many of which
mentation and hypopigmentation; this has been given represent dilated
the name “salt-and-pepper discoloration.” The capil- bronchioles.
lary loops around the nail folds become enlarged and
engorged and are visible without magnification. These
dilated capillary loops occur in up to three quarters of
all patients with progressive systemic sclerosis.
Sclerodactyly is the term given to the progressive
thickness and associated tightness of the digits. It is
caused by the overabundance of collagen production
within the dermis.
Progressive systemic sclerosis is a multisystem dis-
order that not only affects the skin but also causes
significant, life-threatening damage to internal organs.
The esophagus is affected early, and patients complain
of dysphagia and an inability to swallow food easily.
Aspiration of food and liquids is common and often
leads to aspiration pneumonia. Pulmonary fibrosis is
a leading cause of morbidity and mortality. Patients
complain of shortness of breath and a cough. Pulmo- Grossly sectioned lung. Extensive
nary hypertension is almost universally seen. Conduc- fibrosis and multitudinous small
tion defects can develop in the cardiovascular system, cysts. Visceral pleura thickened Esophagus, kidneys, heart, skin, and other
and thickening of the myocardial wall may cause a but not adherent to chest wall organs, as well as joints, may also be affected.
constrictive cardiomyopathy. The kidneys are also
involved, and a subset of patients develop renal failure
and hypertension. on gross evaluation because of the increased amount Treatment: Treatment for this skin disease is diffi-
Pathogenesis: The initiating factor that causes the of dermal collagen. Microscopic evaluation shows an cult. Pruritus can be controlled with antihistamines and
fibroblast to make ever-increasing amounts of collagen increased amount of collagen that replaces everything topical corticosteroids. Ultraviolet phototherapy has
in an unregulated manner is unknown. Many possible including the adnexal structures and subcutaneous fat. been used. The deeper-penetrating ultraviolet A (UVA)
targets are being explored as potential causes of The extensive collagen is so vast that it can appear rays work best. This is often administered in the form
progressive systemic sclerosis, including fibroblasts, as an amorphous eosinophilic mass with nothing of psoralen + UVA (PUVA) therapy. Systemic cortico-
endothelial cells, various environmental antigens, and between the collagen bundles. A sparse inflammatory steroids and nonsteroidal immunosuppressant therapy
internal defects within T cells. infiltrate is present at the interface of the collagen are the main treatment strategies for this disease. Pro-
Histology: The histological findings in the skin are and underlying remaining tissue. Plasma cells may be gressive systemic sclerosis requires a multidisciplinary
characteristic. Punch biopsy specimens are very square prominent. approach to achieve the best therapeutic results.
142 THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS