Page 152 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 152
Plate 4-67 Integumentary System
REACTIVE ARTHRITIS
(REITER’S SYNDROME)
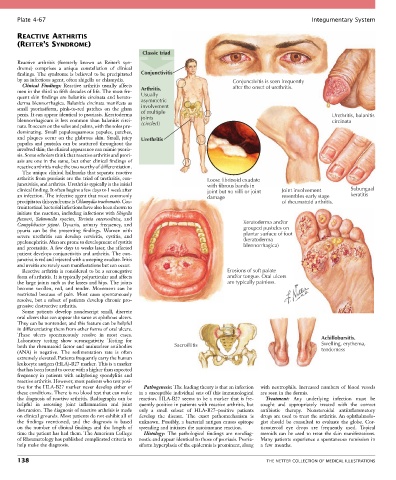
Classic triad
Reactive arthritis (formerly known as Reiter’s syn-
drome) comprises a unique constellation of clinical
findings. The syndrome is believed to be precipitated Conjunctivitis
by an infectious agent, often shigella or chlamydia. Conjunctivitis is seen frequently
Clinical Findings: Reactive arthritis usually affects after the onset of urethritis.
men in the third to fifth decades of life. The most fre- Arthritis.
quent skin findings are balanitis circinata and kerato- Usually
derma blennorrhagica. Balanitis circinata manifests as asymmetric
small psoriasiform, pink-to-red patches on the glans involvement
penis. It can appear identical to psoriasis. Keratoderma of multiple Urethritis, balanitis
blennorrhagicum is less common than balanitis circi- joints circinata
nata. It occurs on the soles and palms, with the soles pre- (circled)
dominating. Small papulosquamous papules, patches,
and plaques occur on the glabrous skin. Small, juicy Urethritis
papules and pustules can be scattered throughout the
involved skin; the clinical appearance can mimic psoria-
sis. Some scholars think that reactive arthritis and psori-
asis are one in the same, but other clinical findings of
reactive arthritis make the two worthy of differentiation.
The unique clinical hallmarks that separate reactive
arthritis from psoriasis are the triad of urethritis, con- Loose fibrinoid exudate
junctivitis, and arthritis. Urethritis typically is the initial with fibrous bands in
clinical finding. It often begins a few days to 1 week after joint but no villi or joint Joint involvement Subungual
an infection. The infective agent that most commonly damage resembles early stage keratitis
precipitates this syndrome is Chlamydia trachomatis. Gas- of rheumatoid arthritis.
trointestinal bacterial infections have also been shown to
initiate the reaction, including infections with Shigella
flexneri, Salmonella species, Yersinia enterocolitica, and
Campylobacter jejuni. Dysuria, urinary frequency, and Keratoderma and/or
pyuria can be the presenting findings. Women with grouped pustules on
severe urethritis can develop cervicitis, cystitis, and plantar surface of foot
pyelonephritis. Men are prone to development of cystitis (keratoderma
and prostatitis. A few days to weeks later, the affected blennorrhagica)
patient develops conjunctivitis and arthritis. The con-
junctiva is red and injected with a weeping exudate. Iritis
and uveitis are rarely seen manifestations but can occur.
Reactive arthritis is considered to be a seronegative Erosions of soft palate
form of arthritis. It is typically polyarticular and affects and/or tongue. Oral ulcers
the large joints such as the knees and hips. The joints are typically painless.
become swollen, red, and tender. Movement can be
restricted because of pain. Most cases spontaneously
resolve, but a subset of patients develop chronic pro-
gressive destructive arthritis.
Some patients develop nondescript small, discrete
oral ulcers that can appear the same as aphthous ulcers.
They can be nontender, and this feature can be helpful
in differentiating them from other forms of oral ulcers.
These ulcers spontaneously resolve in most cases. Achillobursitis.
Laboratory testing show seronegativity. Testing for Swelling, erythema,
both the rheumatoid factor and antinuclear antibodies Sacroiliitis tenderness
(ANA) is negative. The sedimentation rate is often
extremely elevated. Patients frequently carry the human
leukocyte antigen (HLA)-B27 marker. This is a marker
that has been found to occur with a higher than expected
frequency in patients with ankylosing spondylitis and
reactive arthritis. However, most patients who test posi-
tive for the HLA-B27 marker never develop either of Pathogenesis: The leading theory is that an infection with neutrophils. Increased numbers of blood vessels
these conditions. There is no blood test that can make in a susceptible individual sets off this immunological are seen in the dermis.
the diagnosis of reactive arthritis. Radiographs can be reaction. HLA-B27 seems to be a marker that is fre- Treatment: Any underlying infection must be
helpful in assessing joint inflammation and joint quently positive in patients with reactive arthritis, but sought and appropriately treated with the correct
destruction. The diagnosis of reactive arthritis is made only a small subset of HLA-B27–positive patients antibiotic therapy. Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory
on clinical grounds. Most patients do not exhibit all of develop the disease. The exact pathomechanism is drugs are used to treat the arthritis. An ophthalmolo-
the findings mentioned, and the diagnosis is based unknown. Possibly, a bacterial antigen causes epitope gist should be consulted to evaluate the globe. Cor-
on the number of clinical findings and the length of spreading and initiates the autoimmune reaction. ticosteroid eye drops are frequently used. Topical
time the patient has had them. The American College Histology: The pathological findings are nondiag- steroids can be used to treat the skin manifestations.
of Rheumatology has published complicated criteria to nostic and appear identical to those of psoriasis. Psoria- Many patients experience a spontaneous remission in
help make the diagnosis. siform hyperplasia of the epidermis is prominent, along a few months.
138 THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS