Page 187 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 187
Plate 6-12 Infectious Diseases
HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS ENCEPHALITIS
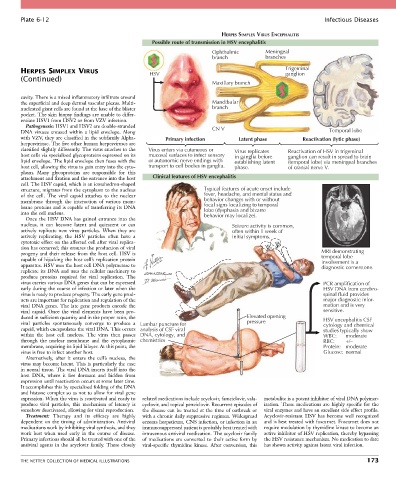
Possible route of transmission in HSV encephalitis
Ophthalmic Meningeal
branch branches
HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS HSV Trigeminal
ganglion
(Continued)
Maxillary branch
cavity. There is a mixed inflammatory infiltrate around
the superficial and deep dermal vascular plexus. Multi- Mandibular
nucleated giant cells are found at the base of the blister branch
pocket. The skin biopsy findings are unable to differ-
entiate HSV1 from HSV2 or from VZV infection.
Pathogenesis: HSV1 and HSV2 are double-stranded
DNA viruses encased within a lipid envelope. Along CN V Temporal lobe
with VZV, they are classified in the subfamily Alpha- Primary infection Latent phase Reactivation (lytic phase)
herpesvirinae. The five other human herpesviruses are
classified slightly differently. The virus attaches to the Virus enters via cutaneous or Virus replicates Reactivation of HSV in trigeminal
host cells via specialized glycoproteins expressed on its mucosal surfaces to infect sensory in ganglia before ganglion can result in spread to brain
lipid envelope. The lipid envelope then fuses with the or autonomic nerve endings with establishing latent (temporal lobe) via meningeal branches
host cell, allowing the virus to gain entry into the cyto- transport to cell bodies in ganglia. phase. of cranial nerve V.
plasm. Many glycoproteins are responsible for this
attachment and fixation and the entrance into the host Clinical features of HSV encephalitis
cell. The HSV capsid, which is an icosahedron-shaped
structure, migrates from the cytoplasm to the nucleus Typical features of acute onset include
of the cell. The viral capsid attaches to the nuclear fever, headache, and mental status and
membrane through the interaction of various mem- behavior changes with or without
brane proteins and is capable of transferring its DNA focal signs localizing to temporal
lobe (dysphasia and bizarre
into the cell nucleus. behavior may localize).
Once the HSV DNA has gained entrance into the
nucleus, it can become latent and quiescent or can Seizure activity is common,
actively replicate new virus particles. When they are often within 1 week of
actively replicating, the HSV particles often have a initial symptoms.
cytotoxic effect on the affected cell after viral replica-
tion has occurred; this ensures the production of viral
progeny and their release from the host cell. HSV is MRI demonstrating
temporal lobe
capable of hijacking the host cell’s replication protein involvement is a
apparatus. HSV uses the host cell DNA polymerase to diagnostic cornerstone.
replicate its DNA and uses the cellular machinery to
produce proteins required for viral replication. The
virus carries various DNA genes that can be expressed PCR amplification of
early during the course of infection or later when the HSV DNA from cerebro-
virus is ready to produce progeny. The early gene prod- spinal fluid provides
ucts are important for replication and regulation of the major diagnostic infor-
viral DNA genes. The late gene products encode the mation and is very
viral capsid. Once the viral elements have been pro- sensitive.
duced in sufficient quantity and in the proper ratio, the Elevated opening HSV encephalitis CSF
viral particles spontaneously converge to produce a Lumbar puncture for pressure cytology and chemical
capsid, which encapsulates the viral DNA. This occurs analysis of CSF viral studies typically show
within the host cell nucleus. The virus then passes DNA, cytology, and WBC: moderate
through the nuclear membrane and the cytoplasmic chemistries RBC: +/–
membrane, acquiring its lipid bilayer. At this point, the Protein: moderate
virus is free to infect another host. Glucose: normal
Alternatively, after it enters the cell’s nucleus, the
virus may become latent. This is particularly the case
in neural tissue. The viral DNA inserts itself into the
host DNA, where it lies dormant and hidden from
expression until reactivation occurs at some later time.
It accomplishes this by specialized folding of the DNA
and histone complex so as not to allow for viral gene
expression. When the virus is reactivated and ready to related medications include acyclovir, famciclovir, vala- metabolite is a potent inhibitor of viral DNA polymer-
produce viral particles, this mechanism of latency is cyclovir, and topical penciclovir. Recurrent episodes of ization. These medications are highly specific for the
somehow deactivated, allowing for viral reproduction. the disease can be treated at the time of outbreak or viral enzymes and have an excellent side effect profile.
Treatment: Therapy and its efficacy are highly with a chronic daily suppressive regimen. Widespread Acyclovir-resistant HSV has become well recognized
dependent on the timing of administration. Antiviral eczema herpeticum, CNS infection, or infection in an and is best treated with foscarnet. Foscarnet does not
medications work by inhibiting viral synthesis, and they immunosuppressed patient is probably best treated with require modulation by thymidine kinase to become an
work best when used early in the course of disease. intravenous antiviral medication. The acyclovir family active inhibitor of HSV replication, thereby bypassing
Primary infections should all be treated with one of the of medications are converted to their active form by the HSV resistance mechanism. No medication to date
antiviral agents in the acyclovir family. These closely viral-specific thymidine kinase. After conversion, this has shown activity against latent viral infection.
THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS 173