Page 372 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 372
1
1
2:1
/09
/09
1
M
M
Pa
2:1
6 A
6 A
/09
q
q
q
3-3
87.
87.
6
/30
/30
xd
xd
6
t
ara
ara
p
p
t
In
c.
c.
a
a
In
p
g
g
e 3
Pa
Pa
g
48
A
A
e 3
48
48
3-3
LWB
LWB K34 0-c 16_ p p pp333-387.qxd 6/30/09 12:16 AM Page 348 Aptara Inc.
33
LWBK340-c16_
16_
0-c
K34
33
348 P A R T III / Assessment of Heart Disease
syndrome. 5,14,15 Sinus bradycardia can be a response to several P waves: Precede every QRS; have consistent shape; may be
medications, including digitalis, -blockers, calcium channel buried in the preceding T wave
blockers, and antiarrhythmics. PR interval: Usually normal, may be difficult to measure if P
The following are ECG characteristics of sinus bradycardia: waves are buried in T waves
QRS complex: Usually normal
Rate: Less than 60 beats per minute Conduction: Normal through atria, AV node, bundle branches,
Rhythm: Regular and ventricles
P waves: Precede every QRS, consistent shape Example: Sinus tachycardia rate, 107 beats per minute
PR interval: Usually normal (0.12 to 0.20 second)
QRS complex: Usually normal (0.04 to 0.10 second) Treatment of sinus tachycardia is directed at the cause. Because
Conduction: Normal through atria, AV node, bundle branches, this arrhythmia is a physiologic response to a decrease in cardiac
and ventricles output, it should never be ignored, especially in the cardiac patient.
Example: Sinus bradycardia, rate 40 beats per minute Because the ventricles fill with blood and the coronary arteries per-
fuse during diastole, persistent tachycardia can cause decreased
stroke volume, decreased cardiac output, and decreased coronary
V 1 perfusion secondary to the decreased diastolic time that occurs
with rapid heart rates. Carotid sinus pressure may slow the heart
rate temporarily and thereby help in ruling out other arrhythmias.
-Blockers are used to treat tachycardia in patients with acute MI
without signs of HF or contraindications to -blocker therapy.
Sinus bradycardia does not require treatment unless the patient is Sinus Arrhythmia
symptomatic. If the arrhythmia is accompanied by hypotension, Sinus arrhythmia occurs when the SA node discharges irregularly.
restlessness, diaphoresis, chest pain, or other signs of hemodynamic It occurs as a normal phenomenon, especially in the young, and
compromise or by ventricular ectopy, atropine 0.5 mg intravenously decreases with age. Sinus arrhythmia is commonly associated with
(IV) is the treatment of choice. Attempts should be made to decrease the phases of respiration: during inspiration, the SA node fires
vagal stimulation, and, if bradycardia is due to medications, they faster; during expiration, it slows. Other than this phasic increase
should be held until their need has been reevaluated. See Chapter 27 and decrease in rate, sinus arrhythmia looks like normal sinus
for the ACLS algorithm for treatment of symptomatic bradycardia. rhythm and it does not require treatment. The following charac-
teristics are typical of sinus arrhythmia:
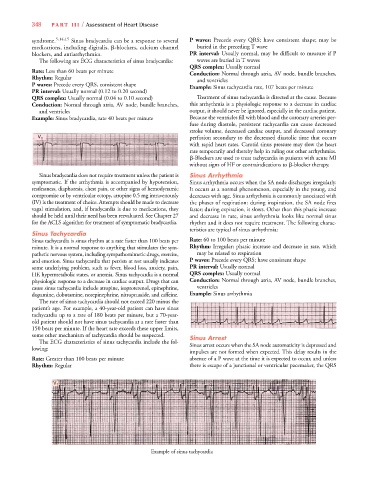
Sinus Tachycardia
Sinus tachycardia is sinus rhythm at a rate faster than 100 beats per Rate: 60 to 100 beats per minute
minute. It is a normal response to anything that stimulates the sym- Rhythm: Irregular; phasic increase and decrease in rate, which
pathetic nervous system, including sympathomimetic drugs, exercise, may be related to respiration
and emotion. Sinus tachycardia that persists at rest usually indicates P waves: Precede every QRS; have consistent shape
some underlying problem, such as fever, blood loss, anxiety, pain, PR interval: Usually normal
HF, hypermetabolic states, or anemia. Sinus tachycardia is a normal QRS complex: Usually normal
physiologic response to a decrease in cardiac output. Drugs that can Conduction: Normal through atria, AV node, bundle branches,
cause sinus tachycardia include atropine, isoproterenol, epinephrine, ventricles
dopamine, dobutamine, norepinephrine, nitroprusside, and caffeine. Example: Sinus arrhythmia
The rate of sinus tachycardia should not exceed 220 minus the
patient’s age. For example, a 40-year-old patient can have sinus
tachycardia up to a rate of 180 beats per minute, but a 70-year-
old patient should not have sinus tachycardia at a rate faster than
150 beats per minute. If the heart rate exceeds these upper limits,
some other mechanism of tachycardia should be suspected. Sinus Arrest
The ECG characteristics of sinus tachycardia include the fol- Sinus arrest occurs when the SA node automaticity is depressed and
lowing:
impulses are not formed when expected. This delay results in the
r
Rate: Greater than 100 beats per minute absence of a P wave at the time it is expected to occur, and unless
r
Rhythm: Regular there is escape of a junctional or ventricular pacemaker, the QRS
V 1
Example of sinus tachycardia