Page 499 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 499
009
009
9/2
9/2
0
8:2
8 A
0
8:2
10.
qxd
10.
10.
qxd
9/0
9/0
0
0
8 A
75
75
e 4
e 4
75
ara
ara
Apt
Apt
P
P
M
M
P
g
g
a
a
LWB
K34
K34
L L LWB
p46
p46
LWBK340-c21_21_p460-510.qxd 09/09/2009 08:28 AM Page 475 Aptara
21_
0-5
0-5
21_
0-c
0-c
K34
C HAPTER 2 1 / Hemodynamic Monitoring 475
SVC RA RV PA LA LV Aorta
Catheter
Catheter
Catheter
Catheter
Catheter
Catheter
Catheter
Catheter
ht
ht
e
e
Catheter
Catheter
h
ht
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P PA
PA
A
A
A
A
PA CatheterCatheter B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B
A
Ct
Ca
Catheter
A
Ct
Catheter
Ct
C
C
25/
25/
25/
25/
25/
25/
25/
2 25/
5
25/
25/
5
25/
2/
2/
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
10
25/
25/
25/
5
10
10
5
25/
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
5/ 010
25/
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
05
0
05
05
05
05
25/0-5
25/0-5
25/0
25/0
25/0
2/
05
05
05
0-5
05 25/0 5 25/ / / 10 0 10
05
0-5
05
05
05
05
0-5
05
25/0
25/0
25/0
25/0
5/0 55
0-5
0
/
25/0
25/0
25/0
25/
25/0
25/0
J
A
PAOP
8-12 mm Hg
RVS PA S
RV
PAS
S
O
P PP
PA
AEDP
P P
P
VEDP
RVEDP PAEDP PAOP
R
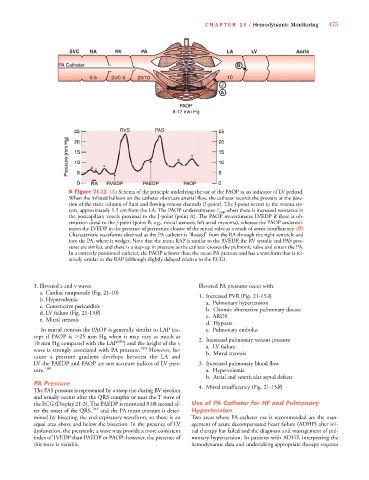
■ Figure 21-12 (A) Schema of the principle underlying the use of the PAOP as an indicator of LV preload.
When the inflated balloon on the catheter obstructs arterial flow, the catheter records the pressure at the junc-
tion of the static column of fluid and flowing venous channels (J-point). The J-point occurs in the venous sys-
tem, approximately 1.5 cm from the LA. The PAOP underestimates P cap when there is increased resistance in
P P
the postcapillary vessels proximal to the J-point (point A). The PAOP overestimates LVEDP if there is ob-
struction distal to the J-point (point B; e.g., mitral stenosis, left atrial myxoma), whereas the PAOP underesti-
mates the LVEDP in the presence of premature closure of the mitral valve as a result of aortic insufficiency. (B)
Characteristic waveforms observed as the PA catheter is “floated” from the RA through the right ventricle and
into the PA, where it wedges. Note that the mean RAP is similar to the RVEDP, the RV systolic and PAS pres-
sures are similar, and there is a step-up in pressure as the catheter crosses the pulmonic valve and enters the PA.
In a correctly positioned catheter, the PAOP is lower than the mean PA pressure and has a waveform that is rel-
atively similar to the RAP (although slightly delayed relative to the ECG).
3.Elevated a and v waves Elevated PA pressures occur with:
a. Cardiac tamponade (Fig. 21-10)
1. Increased PVR (Fig. 21-15A)
b. Hypervolemia
a.Pulmonary hypertension
c. Constrictive pericarditis
b.Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
B
d.LV failure (Fig. 21-13B)
c. ARDS
e. Mitral stenosis
d. Hypoxia
In mitral stenosis the PAOP is generally similar to LAP (ex- e.Pulmonary embolus
cept if PAOP is 25 mm Hg when it may vary as much as 2. Increased pulmonary venous pressure
10 mm Hg compared with the LAP 180 ) and the height of the v a. LV failure
wave is strongly associated with PA pressure. 183 However, be- b. Mitral stenosis
cause a pressure gradient develops between the LA and
LV the PAEDP and PAOP are not accurate indices of LV pres- 3. Increased pulmonary blood flow
sure. 180 a. Hypervolemia
b. Atrial and ventricular septal defects
PA Pressure 4. Mitral insufficiency (Fig. 21-15B)
B
The PAS pressure is represented by a steep rise during RV ejection
and usually occurs after the QRS complex or near the T wave of
the ECG (Display 21-3). The PAEDP is measured 0.08 second af- Use of PA Catheter for HF and Pulmonary
ter the onset of the QRS, 184 and the PA mean pressure is deter- Hypertension
mined by bisecting the end-expiratory waveform, so there is an Two areas where PA catheter use is recommended are the man-
equal area above and below the bisection. In the presence of LV agement of acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) after ini-
dysfunction, the presystolic a wave may provide a more consistent tial therapy has failed and the diagnosis and management of pul-
index of LVEDP than PAEDP or PAOP; however, the presence of monary hypertension. In patients with ADHF, interpreting the
this wave is variable. hemodynamic data and undertaking appropriate therapy requires