Page 500 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 500
9/2
9/2
9/0
0
9/0
0
8:2
0
009
009
0-5
10.
0-5
p46
p46
qxd
0
qxd
10.
10.
8:2
76
76
e 4
g
e 4
ara
ara
Apt
76
Apt
M
P
M
8 A
8 A
a
g
a
P
P
K34
K34
L L LWB
LWB
K34
21_
21_
0-c
0-c
LWBK340-c21_21_p460-510.qxd 09/09/2009 08:28 AM Page 476 Aptara
476 P A R T III / Assessment of Heart Disease
30 30
20 "a" "v" "v" 20
x c "y" "a"
10
10 10
0 0
A
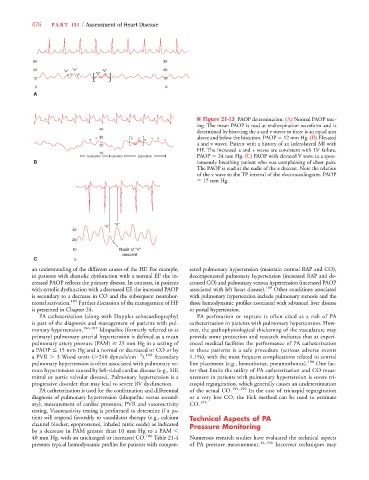
■ Figure 21-13 PAOP determination. (A) Normal PAOP trac-
ing. The mean PAOP is read at end-expiration waveform and is
40
determined by bisecting the a and v waves so there is an equal area
v 30 a v v a above and below the bisection. PAOP 12 mm Hg. (B) Elevated
a a v
20 a and v waves. Patient with a history of an inferolateral MI with
HF. The increased a and v waves are consistent with LV failure.
10
Expiration Inspiration Expiration PAOP 24 mm Hg. (C) PAOP with elevated V wave in a spon-
B taneously breathing patient who was complaining of chest pain.
The PAOP is read at the nadir of the x descent. Note the relation
of the v wave to the TP interval of the electrocardiogram. PAOP
17 mm Hg.
"V"
"a"
30
20
10 Nadir of "x"
descent
C 0
an understanding of the different causes of the HF. For example, sated pulmonary hypertension (maintain normal RAP and CO),
in patients with diastolic dysfunction with a normal EF the in- decompensated pulmonary hypertension (increased RAP and de-
creased PAOP reflects the primary disease. In contrast, in patients creased CO) and pulmonary venous hypertension (increased PAOP
with systolic dysfunction with a decreased EF, the increased PAOP associated with left heart disease). 189 Other conditions associated
is secondary to a decrease in CO and the subsequent neurohor- with pulmonary hypertension include pulmonary stenosis and the
monal activation. 185 Further discussion of the management of HF three hemodynamic profiles associated with advanced liver disease
is presented in Chapter 24. or portal hypertension.
PA catheterization (along with Doppler echocardiography) PA perforation or rupture is often cited as a risk of PA
is part of the diagnosis and management of patients with pul- catheterization in patients with pulmonary hypertension. How-
monary hypertension. 186,187 Idiopathic (formerly referred to as ever, the pathophysiological thickening of the vasculature may
primary) pulmonary arterial hypertension is defined as a mean provide some protection and research indicates that at experi-
pulmonary artery pressure (PAM) 25 mm Hg in a setting of enced medical facilities the performance of PA catheterization
a PAOP 15 mm Hg and a normal or decreased or CO or by in these patients is a safe procedure (serious adverse events
).
a PVR 3 Wood units ( 240 dynes/s/cm 5 188 Secondary 1.1%), with the most frequent complications related to central
pulmonary hypertension is often associated with pulmonary ve- line placement (e.g., hemothorax, pneumothorax). 190 One fac-
nous hypertension caused by left-sided cardiac disease (e.g., HF, tor that limits the utility of PA catheterization and CO meas-
mitral or aortic valvular disease). Pulmonary hypertension is a urement in patients with pulmonary hypertension is severe tri-
progressive disorder that may lead to severe RV dysfunction. cuspid regurgitation, which generally causes an underestimation
PA catheterization is used for the confirmation and differential of the actual CO. 191,192 In the case of tricuspid regurgitation
diagnosis of pulmonary hypertension (idiopathic versus second- or a very low CO, the Fick method can be used to estimate
ary), measurement of cardiac pressures, PVR and vasoreactivity CO. 193
testing. Vasoreactivity testing is performed to determine if a pa-
tient will respond favorably to vasodilator therapy (e.g., calcium Technical Aspects of PA
channel blocker, epoprostenol, inhaled nitric oxide) as indicated Pressure Monitoring
by a decrease in PAM greater than 10 mm Hg to a PAM
40 mm Hg, with an unchanged or increased CO. 186 Table 21-4 Numerous research studies have evaluated the technical aspects
presents typical hemodynamic profiles for patients with compen- of PA pressure measurement. 14,194 Incorrect techniques may