Page 72 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 72
0
0
0
6/3
0/2
0/2
6/3
xd
68.
68.
2-0
q
xd
q
q
009
g
Pa
Pa
g
e 4
e 4
g
Pa
1
1
009
5:3
3
3
5:3
8 A
r
8 A
0-c
02_
r
p
ta
p
p
ta
K34
LWB
LWB K34 0-c 02_ pp042-068.qxd 06/30/2009 15:33 Page 48 Aptara a a
04
04
p
2-0
LWBK340-c02_
p
48 PA R T I / Anatomy and Physiology
Endothelium
Cholinergic
Nitrates
Nitric oxide
M1
(SH)
(SH)
(SH)
(SH)
(SH)
(SH)
(SH)
(SH)
(SH)
(SH)
(SH)
(SH)
(SH)
(SH)
(SH) ) ) ) Opie (2003)
(SH)
(SH)
(SH)
(SH)
(SH)
(SH)
(SH)
H)
H)
(SH)
(SH)
H)
H)
SH)
SH)
SH)
(SH)
(SH)
SH)
( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( (
(SH)
(SH)
(SH)
(SH)
(SH)
(SH)
(SH)
(SH)
(SH)
(SH)
(SH)
(SH)
(SH)
oxide
oxide
c oxide
oxide
oxide
oxide
oxide
nitric oxi
nitric oxi
nitric oxid
nitric oxide
c ic
nitric oxid d d d d ide
nitric oxid
oxide
oxide
oxide
oxide
oxide
xide
xide
xide
oxide
oxide
oxide
oxide
oxide
oxide
oxide
nitric ox
nitric o
nitric ox
nitric o
nitric
nitric
nitric
n
nitr
nit
nitric o
nitric
nitric
nitric
ric
tric
nitric
nitric
nitric
nitric
nitric
nitri
nitric ox
nitric oxide
nitric
nitric oxide
nitric
nitric oxide
nitric oxide
Guanylate
cyclase Ca 2+
Vasodilation
GTP cGMP 2+
Ca channel
(vascular, cardiac)
Mitochondrial respiration
■ Figure 2-5 Nitric oxide messenger system. Proposed role in stim-
ulating soluble guanylate cyclase and cyclic guanosine 3,5 -monophos-
phate to cause vasodilation and possibly a negative inotropic effect.
Antianginal nitrates cause coronary vasodilation by this mechanism.
M1, muscarinic receptor, subtype 1. (From Opie, L. H. [2004]. Heart
physiology: From cell to circulation. Philadelphia: Lippincott.)
Endothelium-Derived Hyperpolarizing Factors. Vasodila- ■ Figure 2-7 Schematic summarizing the release of relaxing factors
tion of arterioles is also mediated by non-NO/non-prostanoid ED- from endothelial cells and their effect on vascular smooth muscle
HFs. 61,62 EDHF may be the predominant mechanism for vasodila- cells. Ach, acetylcholine; A23187, calcium ionophore A21837; BK,
tion in smaller diameter vessels (i.e., resistance arteries 300 m) bradykinin; B2, bradykinin B2 receptor; cAMP, cyclic adenosine
in contrast to larger vessels where NO is the dominant vasodila- monophosphate; cGMP, cyclic guanosine monophosphate; EDHF,
endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor; EET, epoxye-
tor. 63 There are four putative EDHFs: the enzyme cytochrome icosatrienoic acid; K ; potassium channel; M1, M3, muscarinic M1
p450 monooxygenase (cytochrome P-450), potassium, hydrogen or M3 receptor subtypes; NOS, nitric oxide synthase; PGI 2 , prosta-
62
peroxide, and C-type natriuretic peptide. EDHFs, which may be cyclin; P450, cytochrome P450 monooxygenase; TBA, tetrabutylam-
63
considered a mechanism as much as a factor, are synthesized in re- monium; TEA, tetraethylammonium. The broken line indicates the
sponse to wall shear stress or the binding of bradykinin and acetyl- action of an inhibitor or an antagonist. (From Mombouli, J. V., &
choline or substance P to endothelial cell receptors. EDHF diffuses Vanhoutte, P. M. [1999]. Endothelial dysfunction: From physiology
from the endothelium to the vascular smooth muscle where it to therapy. Journal of Molecular Cell Cardiology, 31, 61–74.)
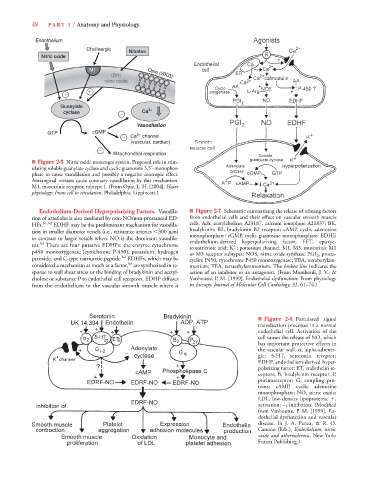
■ Figure 2-6 Postulated signal
transduction processes in a normal
endothelial cell. Activation of the
cell causes the release of NO, which
has important protective effects in
the vascular wall. , alpha-adrener-
gic; 5-HT, serotonin receptor;
EDHF, endothelium-derived hyper-
polarizing factor; ET, endothelin re-
ceptors; B, bradykinin receptor; P,
purinoreceptor; G, coupling pro-
teins; cAMP, cyclic adenosine
monophosphate; NO, nitric oxide;
LDL, low-density lipoproteins;
,
activation; –, inhibition. (Modified
from Vanhoutte, P. M. [1999]. En-
dothelial dysfunction and vascular
disease. In J. A. Panza, & R. O.
Cannon (Eds.), Endothelium, nitric
oxide and atherosclerosis. New York:
Futura Publishing.)