Page 289 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 289
266 P R I N C I P L E S A N D P R A C T I C E O F C R I T I C A L C A R E
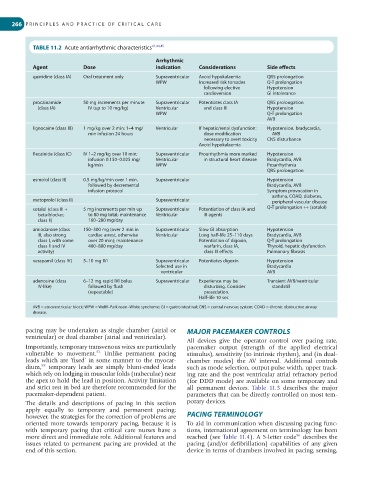
TABLE 11.2 Acute antiarrhythmic characteristics 41,44,45
Arrhythmic
Agent Dose indication Considerations Side effects
quinidine (class IA) Oral treatment only Supraventricular Avoid hypokalaemia QRS prolongation
WPW Increased risk torsades Q-T prolongation
following elective Hypotension
cardioversion GI intolerance
procainamide 50 mg increments per minute Supraventricular Potentiates class IA QRS prolongation
(class IA) IV (up to 10 mg/kg) Ventricular and class III Hypotension
WPW Q-T prolongation
AVB
lignocaine (class IB) 1 mg/kg over 2 min; 1–4 mg/ Ventricular If hepatic/renal dysfunction: Hypotension, bradycardia,
min infusion 24 hours dose modification AVB
necessary to avert toxicity CNS disturbance
Avoid hypokalaemia
flecainide (class IC) IV 1–2 mg/kg over 10 min; Supraventricular Proarrhythmia more marked Hypotension
infusion 0.150–0.025 mg/ Ventricular in structural heart disease Bradycardia, AVB
kg/min WPW Proarrhythmia
QRS prolongation
esmolol (class II) 0.5 mg/kg/min over 1 min, Supraventricular Hypotension
followed by decremental Bradycardia, AVB
infusion protocol Symptom provocation in
asthma, COAD, diabetes,
metoprolol (class II) Supraventricular peripheral vascular disease
sotalol (class III + 5 mg increments per min up Supraventricular Potentiation of class IA and Q-T prolongation ++ (sotalol)
beta-blocker, to 80 mg total; maintenance Ventricular III agents
class II) 160–280 mg/day
amiodarone (class 150–300 mg (over 2 min in Supraventricular Slow GI absorption Hypotension
III, also strong cardiac arrest, otherwise Ventricular Long half-life 25–110 days Bradycardia, AVB
class I, with some over 20 min); maintenance Potentiation of digoxin, Q-T prolongation
class II and IV 400–800 mg/day warfarin, class IA, Thyroid, hepatic dysfunction
activity) class III effects Pulmonary fibrosis
verapamil (class IV) 5–10 mg IVI Supraventricular Potentiates digoxin Hypotension
Selected use in Bradycardia
ventricular AVB
adenosine (class 6–12 mg rapid IVI bolus Supraventricular Experience may be Transient AVB/ventricular
IV-like) followed by flush disturbing. Consider standstill
(repeatable) presedation.
Half-life 10 sec
AVB = atrioventricular block; WPW = Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome; GI = gastrointestinal; CNS = central nervous system; COAD = chronic obstructive airway
disease.
pacing may be undertaken as single chamber (atrial or MAJOR PACEMAKER CONTROLS
ventricular) or dual chamber (atrial and ventricular).
All devices give the operator control over pacing rate,
Importantly, temporary transvenous wires are particularly pacemaker output (strength of the applied electrical
53
vulnerable to movement. Unlike permanent pacing stimulus), sensitivity (to intrinsic rhythm), and (in dual-
leads which are ‘fixed’ in some manner to the myocar- chamber modes) the AV interval. Additional controls
55
dium, temporary leads are simply blunt-ended leads such as mode selection, output pulse width, upper track-
which rely on lodging in muscular folds (trabeculae) near ing rate and the post ventricular atrial refractory period
the apex to hold the lead in position. Activity limitation (for DDD mode) are available on some temporary and
and strict rest in bed are therefore recommended for the all permanent devices. Table 11.3 describes the major
pacemaker-dependent patient. parameters that can be directly controlled on most tem-
The details and descriptions of pacing in this section porary devices.
apply equally to temporary and permanent pacing;
however, the strategies for the correction of problems are PACING TERMINOLOGY
oriented more towards temporary pacing, because it is To aid in communication when discussing pacing func-
with temporary pacing that critical care nurses have a tions, international agreement on terminology has been
56
more direct and immediate role. Additional features and reached (see Table 11.4). A 5-letter code describes the
issues related to permanent pacing are provided at the pacing (and/or defibrillation) capabilities of any given
end of this section. device in terms of chambers involved in pacing, sensing,