Page 121 - 9780077418427.pdf
P. 121
/Users/user-f465/Desktop
tiL12214_ch04_085-114.indd Page 98 9/1/10 9:37 PM user-f465
tiL12214_ch04_085-114.indd Page 98 9/1/10 9:37 PM user-f465 /Users/user-f465/Desktop
CONCEPTS Applied
How Convection Works
A Convection takes place in fluids where a temperature
difference exists. To see why this occurs, obtain a
B
balloon filled with very cold water and a second balloon
filled with the same volume of very hot water. Carefully
put the balloon with cold water in a large container of
hot water. Place the balloon filled with hot water into
a large container of cold water. What happens in each
container? What does this tell you about the relationship
between the temperature and density of a fluid and how
C convection works?
FIGURE 4.15 (A) Two identical volumes of air are balanced,
since they have the same number of molecules and the same
mass. (B) Increased temperature causes one volume to expand
from the increased kinetic energy of the gas molecules. (C) The
same volume of the expanded air now contains fewer gas mol- Radiation
ecules and is less dense, and it is buoyed up by the cooler, more
dense air. The third way that heat transfer takes place because of a tem-
perature difference is called radiation. Radiation involves the
form of energy called radiant energy, energy that moves through
space. As you learned in chapter 3, radiant energy includes
visible light and many other forms as well. All objects with a
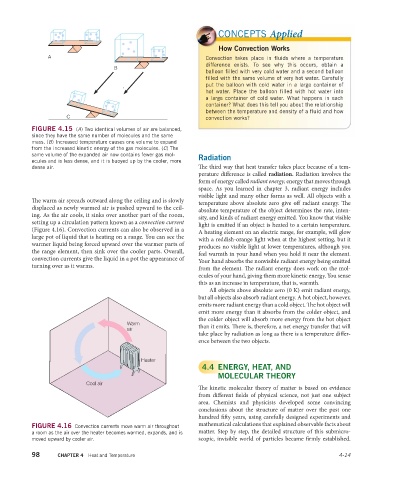
The warm air spreads outward along the ceiling and is slowly
temperature above absolute zero give off radiant energy. Th e
displaced as newly warmed air is pushed upward to the ceil-
absolute temperature of the object determines the rate, inten-
ing. As the air cools, it sinks over another part of the room,
sity, and kinds of radiant energy emitted. You know that visible
setting up a circulation pattern known as a convection current
light is emitted if an object is heated to a certain temperature.
(Figure 4.16). Convection currents can also be observed in a
A heating element on an electric range, for example, will glow
large pot of liquid that is heating on a range. You can see the
with a reddish-orange light when at the highest setting, but it
warmer liquid being forced upward over the warmer parts of
produces no visible light at lower temperatures, although you
the range element, then sink over the cooler parts. Overall,
feel warmth in your hand when you hold it near the element.
convection currents give the liquid in a pot the appearance of
Your hand absorbs the nonvisible radiant energy being emitted
turning over as it warms.
from the element. The radiant energy does work on the mol-
ecules of your hand, giving them more kinetic energy. You sense
this as an increase in temperature, that is, warmth.
All objects above absolute zero (0 K) emit radiant energy,
but all objects also absorb radiant energy. A hot object, however,
emits more radiant energy than a cold object. The hot object will
emit more energy than it absorbs from the colder object, and
the colder object will absorb more energy from the hot object
Warm
air than it emits. There is, therefore, a net energy transfer that will
take place by radiation as long as there is a temperature diff er-
ence between the two objects.
Heater
4.4 ENERGY, HEAT, AND
MOLECULAR THEORY
Cool air
The kinetic molecular theory of matter is based on evidence
from diff erent fields of physical science, not just one subject
area. Chemists and physicists developed some convincing
conclusions about the structure of matter over the past one
hundred fi fty years, using carefully designed experiments and
mathematical calculations that explained observable facts about
FIGURE 4.16 Convection currents move warm air throughout
a room as the air over the heater becomes warmed, expands, and is matter. Step by step, the detailed structure of this submicro-
moved upward by cooler air. scopic, invisible world of particles became fi rmly established.
98 CHAPTER 4 Heat and Temperature 4-14