Page 86 - Class-11-Physics-Part-1_Neat
P. 86
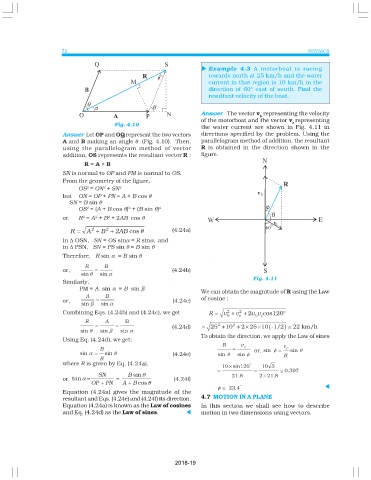
72 PHYSICS
Example 4.3 A motorboat is racing
t
towards north at 25 km/h and the water
current in that region is 10 km/h in the
direction of 60° east of south. Find the
resultant velocity of the boat.
Answer The vector v representing the velocity
b
of the motorboat and the vector v representing
Fig. 4.10 c
the water current are shown in Fig. 4.11 in
Answer Let OP and OQ represent the two vectors directions specified by the problem. Using the
A and B making an angle θ (Fig. 4.10). Then, parallelogram method of addition, the resultant
using the parallelogram method of vector R is obtained in the direction shown in the
addition, OS represents the resultant vector R : figure.
R = A + B
SN is normal to OP and PM is normal to OS.
From the geometry of the figure,
2
2
OS = ON + SN 2
but ON = OP + PN = A + B cos θ
SN = B sin θ
OS = (A + B cos θ) + (B sin θ) 2
2
2
or, R = A + B + 2AB cos θ
2
2
2
2
2
R = A + B + 2AB cos θ (4.24a)
In ∆ OSN, SN = OS sinα = R sinα, and
in ∆ PSN, SN = PS sin θ = B sin θ
Therefore, R sin α = B sin θ
R B
or, = (4.24b)
sin θ sin α
Fig. 4.11
Similarly,
PM = A sin α = B sin β
We can obtain the magnitude of R using the Law
A B
or, = (4.24c) of cosine :
sin β sin α
2
2
Combining Eqs. (4.24b) and (4.24c), we get R = v + v + 2 v v cos120 o
c
b c
b
R A B
(
×
×
2
2
= = (4.24d) = 25 + 10 + 2 25 10 -1/2) ≅ 22 km/h
sin θ sin β sin α
To obtain the direction, we apply the Law of sines
Using Eq. (4.24d), we get:
R v c v
B = or, sin φ = c sin θ
sin α = sin θ (4.24e) sin θ sin φ R
R
where R is given by Eq. (4.24a). 10 sin120 10 3
×
= = ≅ 0.397
×
or, tanα = SN = B sinθ (4.24f) 21.8 2 21.8
OP + PN A + B cosθ
φ ≅ 23.4 t
Equation (4.24a) gives the magnitude of the
resultant and Eqs. (4.24e) and (4.24f) its direction. 4.7 MOTION IN A PLANE
Equation (4.24a) is known as the Law of cosines In this section we shall see how to describe
and Eq. (4.24d) as the Law of sines. t motion in two dimensions using vectors.
2018-19